Google News is a news aggregator. It was created to deliver quick news to search engine users after the demand spiked post-9/11. Started as one of Google’s many test projects, it gained the recognition of managers and was officially launched in 2002. Currently, Google News aggregates breaking news in over 120 countries and dozens of languages.
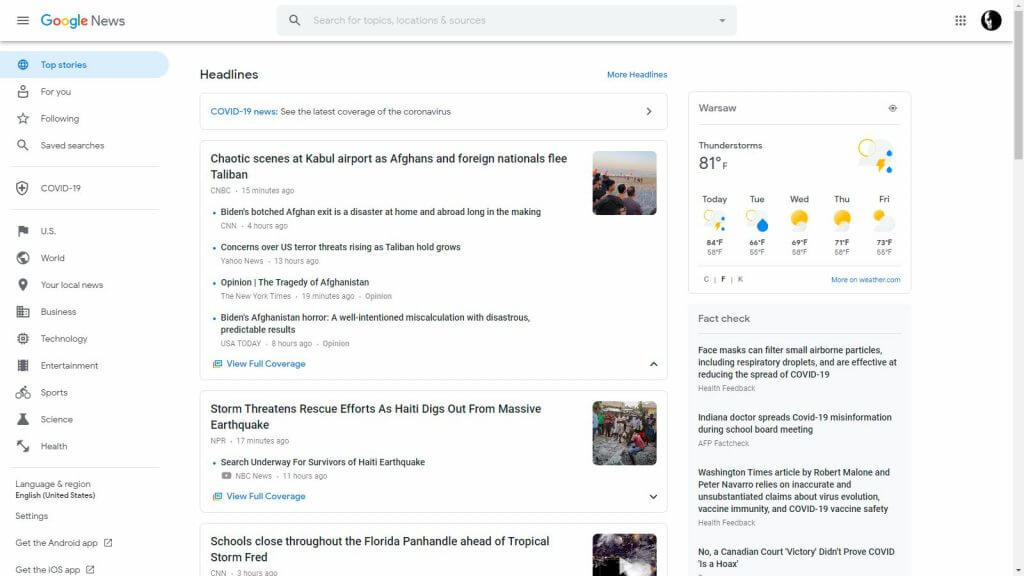
Google News web for desktop – from news.google.com
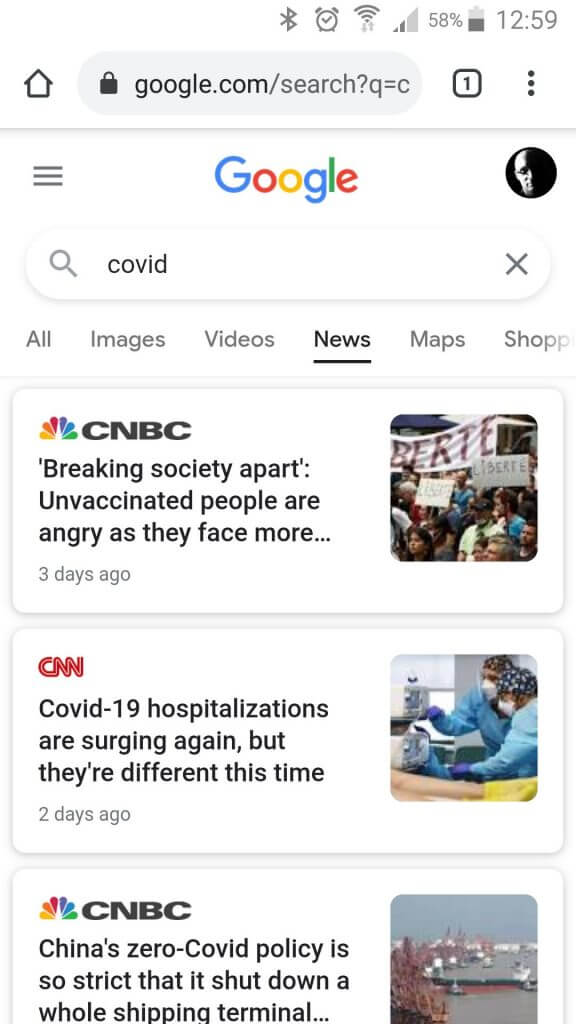
Google News for web – mobile
But Google News is not only an aggregator of news from around the world – it is also the Top Stories widget you see in search engine results, a separate tab in search results, and an app. In this article, I’ll focus mainly on Top Stories.
What’s the difference between Top Stories and Google News?
Top Stories is based on an algorithm which expands your search results – both on mobile and desktop – when the given search topic starts getting popular (more on that later). The widget mainly shows news services from Google News, but not only – sometimes Reddit, Twitter and other non-news services make an appearance.
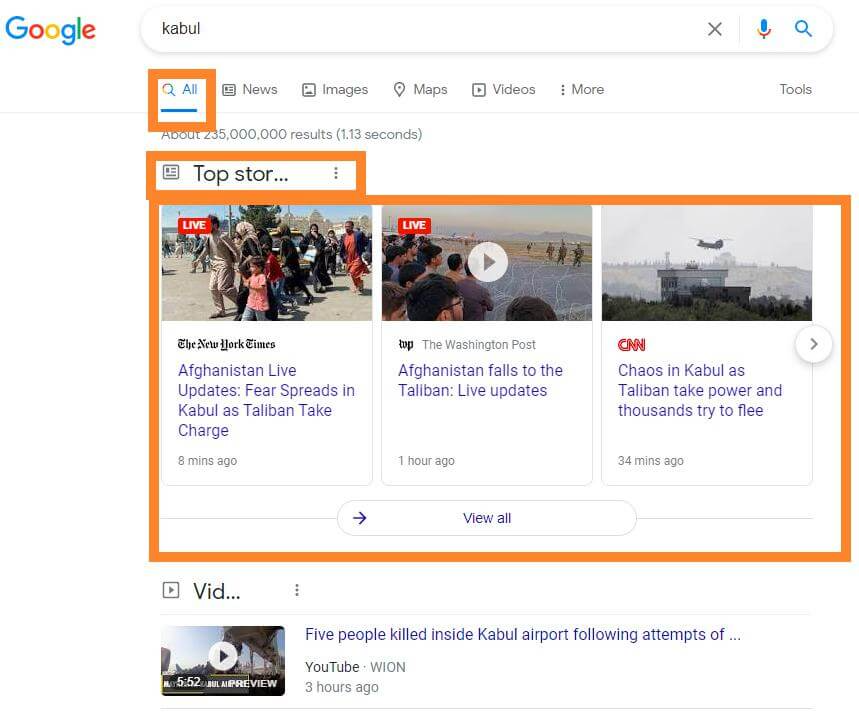
Top Stories for desktop devices
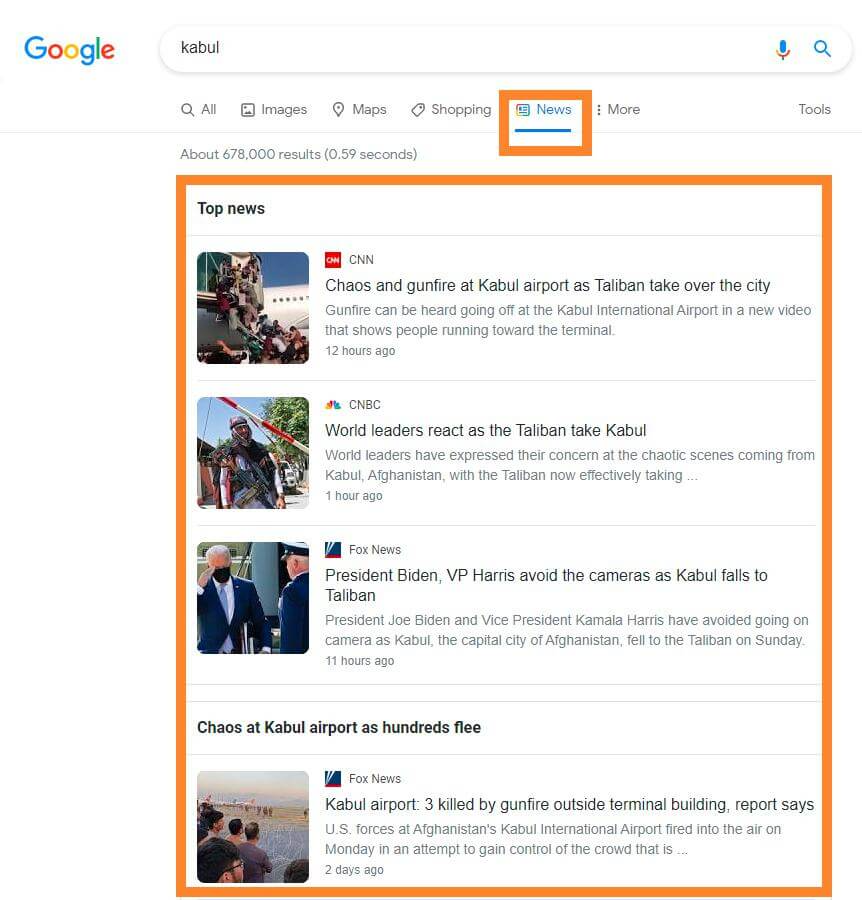
And this is what the content of the News tab looks like for the same phrase.
Top Stories and Google News are very often confused. Colloquially, the Top Stories widget is sometimes referred to as Google News.
Personalizing your Top Stories results
It’s possible to personalize Top Stories results, but that’s fairly limited compared to other Google services. What matters more is the type of the device you’re using.
Mobile vs. desktop
Top Stories widgets appear in both desktop and mobile search results. The results for the same phrase may differ depending on device type. In addition, right now, to stand a chance of getting to the Top Stories carousel on mobile, your article must be in the AMP version. Google is supposed to retire this requirement some time next year, but it is uncertain when, or if it will be permanent.
When are Top Stories displayed?
Dynamic Top Stories results are not generated for every phrase. Even a phrase which generates a Top Stories block today may not do so tomorrow.
The mechanism responsible for this analyzes hundreds of thousands of phrases entered by users every day. It selects those which grow faster than some threshold value. The process is completely automatic and can be influenced. For instance, a publisher owning multiple news sites can cause a specific phrase to generate a block.
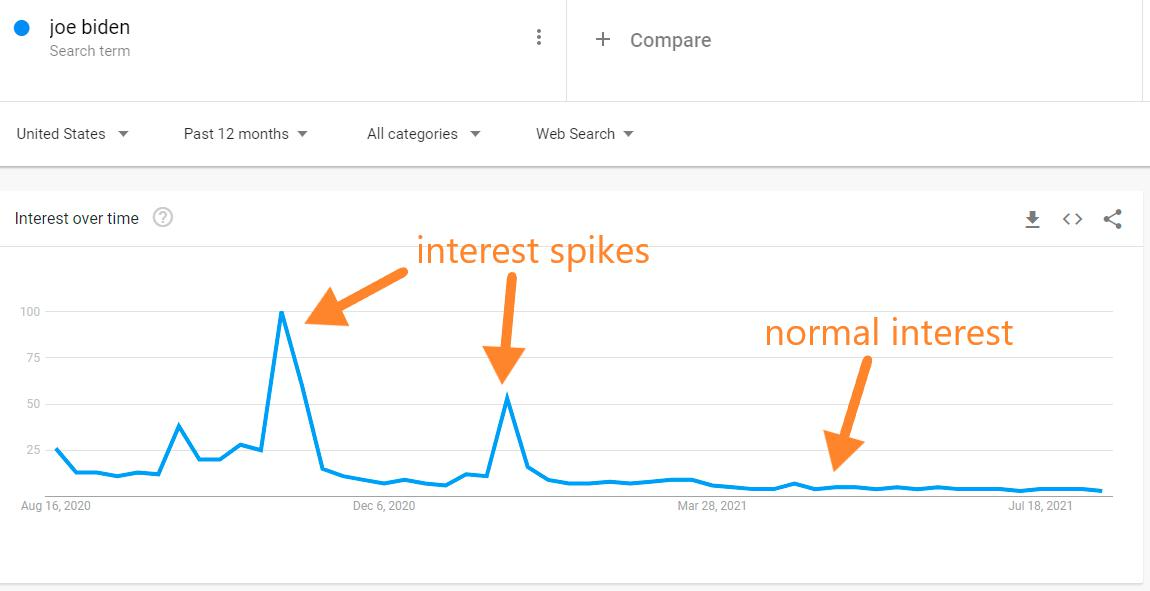
Interest in the phrase Joe Biden in the last 12 months (16 Aug. 2021). Source: Google Trends
When can this mechanism be used? For example, when we’re launching a new website or service. It requires a dozen or so websites to publish articles on the same topic at a similar time (articles should be unique, i.e. we do not publish one and the same article everywhere). I have used this hack several times to break through with information about a new site or service.
Can evergreen material appear in Google News?
Yes, if it meets a few conditions – the publication must be fresh and the topic must hit a trend.
For example: “how to break a fever in a child” is a typical evergreen topic that can become trendy if something like the Covid-19 epidemic happens.
Do only large sites stand a chance to appear in Google News?
Theoretically, any website that publishes news-type materials can make it into Top Stories. Websites with great authority, i.e. well-known brands that are strongly linked, have the best chance.
The website must also meet the technical requirements of Google News (more on that below) and publish materials about current events.
For example, an online store selling smartphones may set up a news section on latest events, premieres, and news about smartphones. Just remember not to spam, but provide valuable content for the readers. The Google News publishing rules also state clearly that you cannot publish sales material there. Is sponsored material eligible? Ask your lawyer and read the terms of service carefully.
Why are Top Stories important for publishers?
Google News brings its users thousands of articles and materials on current events around the world. People can quickly get the latest information from many different websites in one place. This means that millions of readers consume this content every day. One article can generate up to half a million visits from the Top Stories block. You can see why it is a tasty morsel for practically every news site. It gets top publishers up to 50% of their traffic.
What’s important from the publisher’s point of view?
To appear in the Top Stories block, you have to be fast. You should respond to trends and events straightaway. Remember that the results in the Top Stories block rotate at the speed of light and in the case of a very strong trend, e.g. an accident or a terrorist attack, they can change every few minutes.
Google News constantly needs new information. A few years ago, this led to a popular exploit cheating the algorithm by recurrently changing the URL and publication date of the same article. (This, of course, no longer works, and if used a lot may be grounds for exclusion from the GN service, including Top Stories).
Vulnerability of Google News algorithms
Unfortunately, Google News algorithms are not updated as often as the main Google search engine. This means that a lot of publishers out there keep cheating Google’s mechanisms, and by the same token – deceiving users. I won’t name any names, because I assume that most of us came across such materials at one time or another.
Google Trends and Google News
A useful tool for tracking trends in the Google search engine is Google Trends. It is a free tool that aggregates information about user queries and groups articles into topics. It shows which topics were most popular in the last few days and also lets us see what’s trending now. Using this and other trend-finding tools is a topic for a separate article.
Google News and copyright
From the beginning, the service aroused controversy among publishers, who filed lawsuits against Google for copyright infringement. The right to download photos and excerpts from articles and display them in aggregate was argued before courts several times, where the cases usually ended in settlement and the Google service continued to work.
A dispute brought by Spanish publishers had an interesting result, as Google closed the GN service for Spanish websites. By removing problematic websites from its service, Google cut off traffic to them. The issue is now coming back with redoubled strength – this time Google must contend with EU bureaucrats, not just a single country. A potential blockade of the entire EU would constitute a much larger loss of market for Google than Spain alone.
How to get on Google News?
To be featured on the Google News service always means that your website or its section must be dedicated to news. Technically, this requires you to:
-
set up a profile in the Publisher Center
-
fill in the application form (it is described step by step),
-
verify the right to the domain (via Google Search Console) and pass the verification. It is semi-automatic – a person makes the final determination.
-
After positive verification, your articles will start appearing in the “News” tab of the search results. You can check this by typing the known search operator site:domain.com in the search field. If everything is ok, you will see links to your publications.
Google strives to eliminate the need for manual verification. The service shows more and more individual materials from websites that are not typical news sites.
Google News and paywall
Google News also allows websites which reserve content behind a paywall. On such sites, the user gains access to the content after meeting the publisher’s conditions, like setting up a free account, purchasing one-time access, e.g. via text message, or purchasing a monthly subscription.
However, in order for a website to appear in the search results and the Google News block, it must meet some technical requirements (see below). An additional condition is giving the Google bot access to the full content of the articles.
More than 10 years ago, Google offered the option of reading 5 articles for free per month, after which the reader had to pay. Currently, Google lets each publisher set its own policy.
Top Stories and analytics
Traffic analysis from the Top Stories block is a difficult thing to do. Clicks can be seen in Google Search Console and in Google Analytics, but distinguishing traffic generated by the block versus the usual links from Universal Search is not that easy. There is no tool that will clearly indicate which visits were from the block and which from blue links (i.e. ordinary text links in search results) or other places.
Isolating traffic from Top Stories is made extra difficult by the fact that a link presented in the carousel may be demoted to blue links under the carousel and still generate visits. There are mathematical models, e.g. time sequence comparison, which help to identify such materials (we are working on developing a tool like this).
Ranking factors in Google News
According to Google, these are:
-
Relevance of content
-
Prominence
-
Authoritativeness
-
Freshness
-
Location
-
Language
Ranking factors for Top Stories
-
keywords
-
entities:
- persons
- events
- organizations
- places
- things
- concepts
- headlines
-
trusted sources
-
topic authority
-
AMP (for mobile)
Technical requirements for Top Stories and Google News
-
AMP (mobile)
-
LiveBlogPosting
-
schema for paywall
- date stamps (Schema)
- datepublished
- datemodified
- picture/graphics url
-
static and unique urls
-
XML sitemap for Google News
-
monolingual (articles in one language)
-
internal linking
-
content freshness
-
no redirects
-
article title and headlines
-
lead/introduction (first paragraph of text)
Other Google News requirements
-
first of all, read the documentation
-
the type of content published on the website or section must be news
-
content should be high-quality, original, and up-to-date
-
content must comply with the Google News policy
-
the website should have an XML map dedicated to Google News – note, it is slightly different from the sitemap for Google Search Console
-
the website should have an “about us” page with data about the editors, chiefs, and the physical address of the editorial office
-
the key element is the date – presented on the page itself, as well as marked with the schema and given in the sitemap
-
the website cannot present pornographic content
-
publications must be regular and frequent enough (depends on the subject and on competition)
-
the website must be submitted to https://publishercenter.google.com/ and be verified – passing verification guarantees being shown in Google News (but not in Top Stories)
Google mechanisms are not public and there are no clear guidelines, e.g. what is an appropriate frequency of publication, what counts as news, etc. Some requirements can only be determined by trial and error.
 Jakub Sawa
Jakub Sawa