What is the point of SEO-friendly copywriting?
SEO copywriting is the creation of content optimized for search engines such as Google. This type of copywriting has become popular, but it may stir up an image of presell pages and poor substance. Ten years ago, this vision could stand to reason. But SEO copywriting has gone a long way.
Today, all online content should be optimized for search engines. To get user attention, the piece needs to include relevant keywords in the right density. Besides, it must present a comprehensive take on the subject – preferably broader than the competition. Good SEO copywriting does not produce poor quality texts, and skilful exploration of new keywords can only ameliorate the content.
The role of content on the website
You probably heard more than once that your content needs to be valuable – from the perspective of both users and Google algorithms. Ideally, you should have a blog, but also category descriptions, full-blown landing pages for your services, and detailed product descriptions. But what’s the point of all that?
There’s a popular belief that most netizens don’t read long texts online, as they focus on the visual layer and appreciate minimalism. Luckily, this view also has a good number of opponents – and that’s how we get to SEO copywriting.
Its main role is to inform Google robots about the content of your website and the keywords you wish to target in the search results.
GoogleBot deals wonderfully with content in all languages. With that in mind, you can use SEO copywriting to build up your visibility in Google and other search engines such as Bing or Yandex.
Visibility => traffic => conversions
Reportedly, 3 billion people use Google worldwide. That’s around 42% of the entire population of the Earth! These are the people you can reach with your products and services as your listing shows up in the first pages of the search results.
The content on your website has a powerful impact on the rank you’ll occupy for different keywords. That means that SEO copywriting can generate precious website traffic. You can keep track of every click on your Google listing with analytical tools – Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Properly implemented analytics will show you on the fly if the new content helps increase your traffic and whether or not that traffic is valuable (in other words, whether it generates macro- or micro-conversions on your website or not).
But traffic alone won’t do you any good. What you need are conversions: purchase transactions, phone calls about your services, or filled-out forms. SEO copywriting and the right keyword optimization will connect you with people looking for the products or services you’re offering! This, in turn, will directly affect your sales by increasing the number of conversions.
Brand recognition
Expertise on SEO copywriting will help you both in the early days, when you’re establishing your online presence or launching a new blog, and later on, when your website has been online for quite some time. You may promote it in many ways, both offline and online. Be active in social media, experiment with email marketing etc. Our word of advice is: try and test!
But Google search results are also a great place to boost your brand recognition when you’re just starting.
Relevant and SEO-friendly content may get you a spot in the search results among the top players on the market. The users won’t need to know anything about your company to find your website. Top-quality SEO copywriting ensures the influx of visitors interested in a particular service or products – all thanks to the right choice of keywords! If your product or service meets user expectations and you provide appropriate customer support, the visitors are bound to remember you for a long time. Maybe next time, instead of looking for what they need in the search engine, they’ll go straight to your website!
Benefits for e-commerce
E-commerce businesses also need proper SEO copywriting.
We have in mind more than product descriptions. Think category descriptions and a blog.
Why can’t you copy-paste descriptions on different pages? Why have a blog if all you need is sales? Isn’t writing category descriptions going over the top?
Remember that every page on your domain falls under the scrutiny of Google, which analyses websites and sets their ranks in the search results. Larger amounts of valuable content on individual pages will improve your ranks, which will translate to greater organic traffic and more conversions.
Your category descriptions should be elaborate. Why?
Long content in an online store allows you to show up in the search results for more and more keywords. In turn, improved search engine visibility helps you reach new users. If your category description has 2 sentences, it will probably contain only one keyword – a bare category name, with no synonyms or linguistic variants. But if you write a category description that’s several thousand characters long, includes long-tail keywords, and provides links to your other pages, the potential for search engine optimization goes through the roof!
It’s also a good idea to run a blog where you can position yourself as an industry expert, drum up brand recognition, and send users to product pages to generate sales. Following the guidelines on SEO copywriting will boost your reach and speed up your SEO efforts, leading to sales.
Benefits for service providers
The imperative to publish elaborate content on a business site often clashes with the vision of business owners or UX designers. They may envisage a short description of services and a one-page layout, with all the necessary information stuffed on the homepage. Yet, the point of SEO copywriting is to create a lot of texts, each focused on one service only. Each new piece of content, armed with carefully selected keywords, should go to a separate page. That is to say that you need to break down your website into many pages, each optimized for one group of keywords.
Why is it so important?
Google needs clear information about the content of each page. A well-developed site structure – achieved by splitting your offer into several or several dozen pages – boosts your chances for high Google ranks for many keywords. Conversely, stuffing one page with many keywords (not synonymous or linguistically related) will bring underwhelming results as the SEO juice will get diluted among all the phrases.
Case in point:
Say you offer cosmetic treatments for the face, the feet, and the body. In such a case, a good SEO practice tells you to create pages for every body part:
- cosmetic facial treatments
- cosmetic hand treatments
- cosmetic foot treatments
- cosmetic body treatments.
Once you’ve created the pages, you move to the realm of SEO copywriting. Just listing the names of offered treatments (all of which should also have dedicated pages) won’t do the trick. Every page needs content that zeroes in on a single service category. Later on, we’ll tell you how to choose the right keywords for that content. Relevant and dedicated texts give you a chance of seeing that page in the TOP 10 listings in the search results.
Benefits for B2B
In the B2B sector, SEO copywriting may be a great resource for lead generation. However, even if you provide top-quality content, it’s best to optimize it already at the writing stage.
How to create B2B content?
Start with your target group. Who reads your content? Is it business owners, managers, or specialists? Each group could have different goals and decision-making authority in the company. What are their needs and what solutions they may be looking for?
To learn more about your target audience, conduct keyword research. It is a process of pinpointing the keywords searched by your future clients. Keyword research is performed with dedicated tools such as Senuto.
Try to saturate your content with long-tail keywords, repeating them several times across the text. Your description of the topic should be exhaustive to build your position as an expert and inspire trust among your potential client base. Google algorithms will also appreciate big quantities of valuable content and repay you with high ranks in the search results.
What content to put on your website?
Product descriptions
A product card is a perfect spot for valuable SEO content relevant to your products. Every page at your online store should have a unique description. Even if your products fall within the same category, each one is different. Product descriptions should zero in on these differences. A detailed product description with relevant keywords, composed according to these guidelines, will allow users to find your store a lot faster. If the product page is optimized for the search term, the visitor will see the desired product right away, with an option to make the purchase.
Bad practices:
If your online store presents nothing but specification tables plus 1–2 sentences generally describing your product – your website still has a lot of untapped potential!
An example of a SEO-friendly product description:
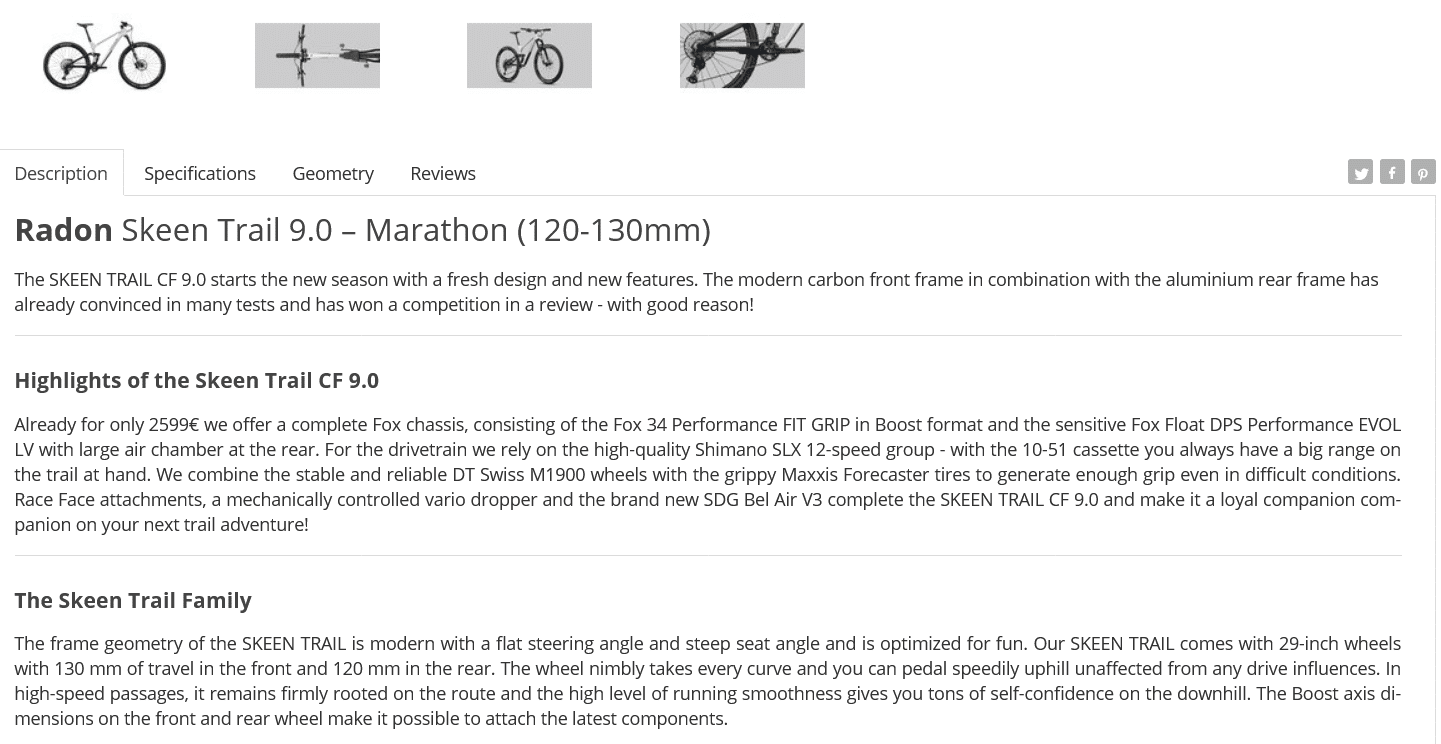
Source: https://www.bike-discount.de/en/buy/radon-skeen-trail-9.0-1060127
Category descriptions
Every category page in your store should have some space for a unique block of text. If you fill it with a description, that category page stands a better chance of showing up on Page One of the search results for the category name and synonymous keywords. It is especially important if your shop offers many similar products. The potential of category descriptions should be unlocked to build up long-tail keywords for a particular product. You may split the descriptions into parts, and place them above or below the product list. The descriptions work great with internal linking implemented within the text.
Bad practices:
We don’t recommend optimizing product pages for general keywords. Such an approach is a frequent cause of traffic drops. A visitor who has typed a general keyword in Google does not know which product they’re interested in buying yet. They want to see the options.
An example of a SEO-friendly category description:
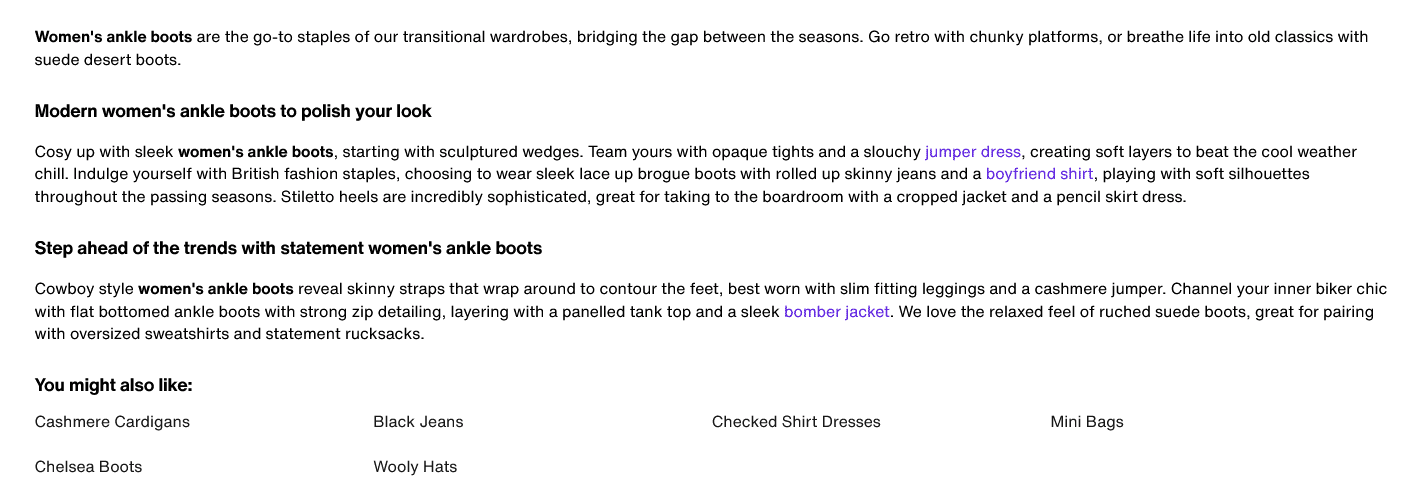
Content for offer pages and information pages
Businesses other than online stores – such as service providers – should have an SEO strategy ready at the stage of website planning. Ideally, they should create a new page with SEO-friendly content for every service. This strategy will work for most business websites and affect the proper growth of website visibility in the search engine. Remember to ensure the right text length, keyword density, subheaders, and all other Google ranking factors described later on in this article.
Bad practices:
Many new websites follow the one-page design. The entire content shows up at the same URL. Such a website stands a poor chance of getting to the top positions in Google, especially if your competition boasts a developed site architecture and publishes a lot of content.
Landing Pages
If you have a product you’d like to promote not only on your domain but also with the use of Google Ads campaigns and simply other websites, consider getting a landing page. It’s nothing more than a target page displayed to a user who clicked on the ad. It usually promotes only one product or service and has nothing to do with other tabs. A landing page is an extension of the ad clicked by the user, so it must present content that sells. That content should also be optimized for search engines. SEO-friendly content will turn your landing page into another high-ranking URL in the search results, listed next to your website’s main offer.
Bad practices:
Some landing pages may have not enough text content. Many companies focus on the eye-catching graphics but forget about the substance. It’s a mistake which limits our potential to establish search engine visibility of such pages.
Blog posts
A blog is no longer just a hobby! Your blog may be a platform for providing stimulating content to people who use your services or buy your products. By answering questions that matter to your users, you position yourself as an expert – which gives you extra points in Google. You don’t know what to write about? The next chapter presents methods and tools for finding attractive topics. The articles can boost your brand awareness and visibility for new (long-tail) keywords. With internal linking, they will also increase your SEO juice and the ranks of your other pages in the search results.
Bad practices:
When starting a blog, watch out for cannibalization. What’s that? Your website should include no two pages optimized for the same keyword. When you publish a blog post about a product or a product category available in your store, you may notice huge reshuffles in ranks for the related keywords. Googlebot will not know which link to display in the search results. To avoid that, try to create blog posts with unique keywords – product names and category names are out.
An example of an SEO-friendly blog:
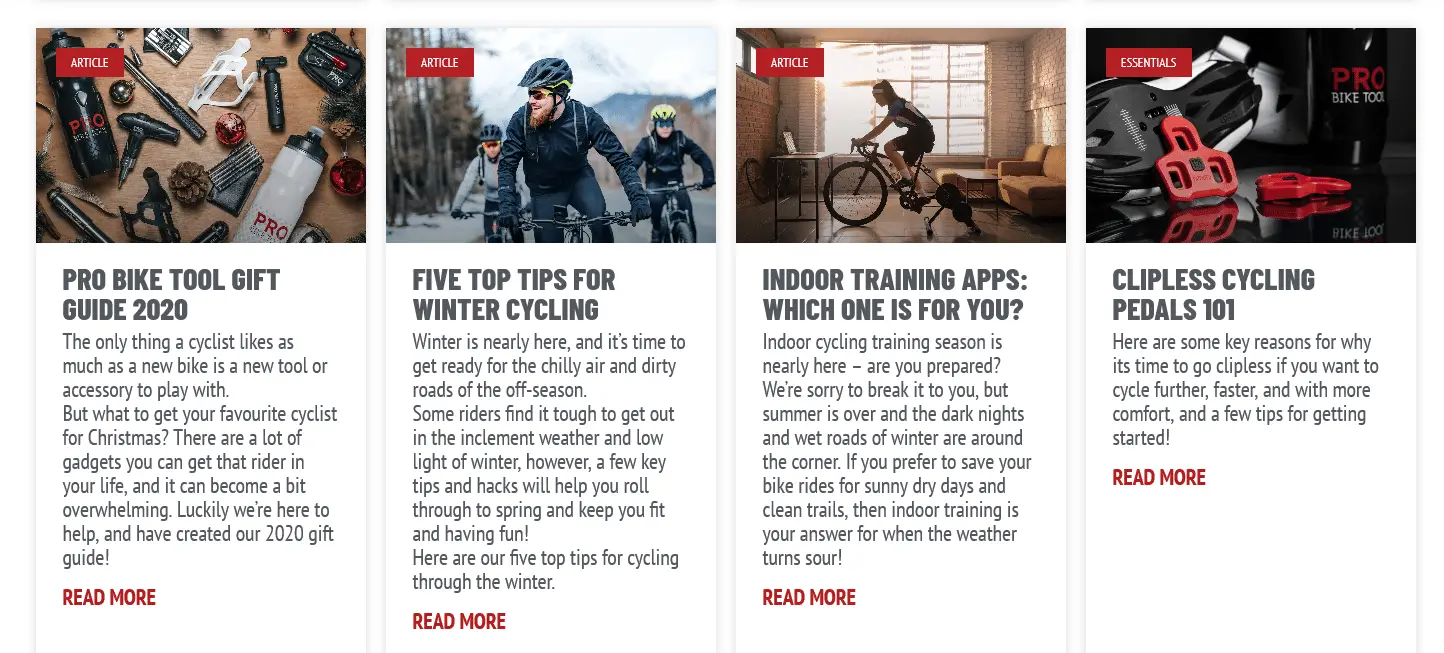
Guides
Are you a specialist in a highly technical industry? Or maybe a manufacturer wishing to reach a specific group of professionals? You have a valid alternative to a lifestyle blog – a series of guides. They may provide an exhaustive overview of a chosen topic or a detailed walkthrough to solving a particular problem. You’ve already published something like that, but offline? Split your materials into portions and post them on your website in a suitable tab. With a subtle SEO facelift, they may turn into successful traffic drivers and work like a blog!
Magazine and neswpaper websites are a common example of where offline publications complement online content:

White papers
A white paper includes documents with aggregated data on a particular industry and their detailed analysis. It may be a source of precious information. Though used mainly to educate the recipient of the product/service, it has high marketing value. A white paper may provide you with useful content that draws user attention and extends visit time. In our experience, both bounce rate and session time may affect SEO results. White papers are a great idea for manufacturers and specialists – just like guides. As for the data sources for your analysis or report, you have multiple options.
Google News
If you own an information web portal and publish new content all the time, you should take a closer look on Google News. The service allows you to reach a huge number of new users and substantially improve your brand recognition. Google News articles show up at the top of search results, so most traffic goes directly to your website. Alas, the feature is not for everyone. You need to meet a set of rather stringent criteria (stylistic and technical) to qualify.
First, your website must be a typical information portal. Google verifies all websites manually, so business sites and blogs stand zero chance. Besides, the texts must be right on the facts, correct in terms of grammar and spelling, signed, and provided with an image and date published. SEO copywriting also plays a role. The right choice of keywords for the title and the body of the article will affect its GN position. Apart from conducting your standard keyword research, find inspiration in the current web trends, basing on data from Google Trends.
What to write about? – SEO advice
As you’re getting down to SEO copywriting, try to envisage your content marketing strategy. Imagine your readers right from the start. After you’ve established the personas, you will be able to prepare content for the people who actually use your services or products. Before you begin, don’t forget to check other, technical aspects of SEO on your website to make sure that the robots will see what’s there. You could also define the mission for your SEO copywriting and the ROI (return on investment). Then, implement the analytical tools (Google Search Console, Google Analytics) to keep track of the effects and give yourself an opportunity for optimization.
Keyword Research – analyze your keywords
The SEO-friendly content you publish online must be based on keyword research. You can conduct it with tools such as Senuto and Google Keyword Planner, which will show you the monthly number of searches for particular keywords. Other useful tools for the job include Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
Key points to keep in mind when doing keyword research:
- Keywords with the highest number of searches will be tempting. Of course, getting to Page One for such queries is a worthy goal. But your competitors are likely to target them as well. Besides, they may not always convert, as users who type them in Google are not yet interested in making a purchase. For this reason, direct your attention to more detailed keywords (long-tail). If you’re preparing product descriptions for an online store, try to choose keywords including several words and features. Instead of starting with a general query – “rings” – go for a more complex phrase such as “engagement ring with blue stone”. The number of monthly searches will be lower, but the effects will come faster. You’ll see better ranks, traffic, and sales.
- Consider the basic makeup of your target keywords:
– brand and general keywords for the homepage,
– keywords related to category names,
– keywords related to product/service names,
– keywords related to the cities you operate in,
– blog keywords (not targeted elsewhere on the website).
Adequately prepared site structure will save you some time in the future and prevent cannibalization, which occurs when several pages target the same keywords and thus hamper each other’s positions in the search engine. As you start working on site architecture and keyword selection, you’ll notice patterns in titles or headers structure. These patterns will allow you to implement global changes across the website.
- Start your optimization by creating a keyword cloud for a particular topic. For instance, if you’re running a mesotherapy business, pinpoint the main keyword that best describes a selected service, and then concretize it with a cloud of thematically related long-tail keywords. Optimize the relevant page for these keywords and start acquiring valuable links… Repeat the procedure for each new page.
Keyword research is a long, time-consuming process. Oftentimes, it’s that part of the SEO efforts that never ends if you wish to steadily increase your visibility and reach new users.
Cooperation with other company departments
Your strategy should be communicated to all company departments. It may help you find employees who know everything about the products, keep in touch with the clients, or have long years of experience in the industry. Brainstorming, collecting ideas, and learning about the most frequent questions answered by the call center department will provide you with a pool of content topics.
Don’t forget to verify if these topics are researched by Google users – the right wording of the titles (including keywords!) will give them more SEO value. If you’re outsourcing content production to external copywriters, all extra guidelines will affect the final outcome. Without cooperation with departments responsible for the product, content, and PR, you’ll have a hard time getting satisfactory results. SEO copywriting, though written mainly for search engine robots, should be valuable also for the users. All in all, it is them who purchase your products or use your services.
Real-time marketing
Pique the interest of your users by discussing topics that are currently trending. Basing your articles on recent news or events gives you an opportunity to outdo your competition. Try it to increase the recognition of your blog or website. Proper search engine optimization of the content and rapid response to current events may guarantee you a spot on Page One. Trending topics get tons of searches and generate huge traffic – which is especially important if you set your sights on Google News.
Competition
You’re out of topic ideas? Looking for inspiration? It never hurts to see what your competitors are writing about. Maybe some topics exciting for your target industry are waiting for you on your rival websites? Needless to say, your text must be unique. In the best-case scenario, it should provide a more detailed account of the topic than your competitors. If you compose in line with SEO copywriting rules, it may outrank the text that gave you the inspiration.
SEO ranking factors
H1 headers
Depending on the type of content, your H1 header may take up different forms:
– H1 Product card = product name,
– H1 Category = category name,
– H1 Article = article title
and so on.
Every page should have one H1 header with a keyword – preferably in a non-inflected form. If you’re writing an article, this may be a challenge. Many article titles sound great but say nothing about the content. If you’re aiming for searchable content, better steer clear of “mysterious” or “enigmatic” titles.
The TITLE tag
The title (H1 header) displayed on your website may differ from the one you present in the search results – the <title> tag. In the best-case scenario, the title tag:
- has slightly different wording than the H1 header,
- contains keywords,
- contains a CTA (call to action),
- ends with your brand name,
- is concise (1–150 characters according to Google) – the titles should not be elaborate. Otherwise, the last words will probably get cut out in the search results. Remember to put your main keywords at the front.
H2 and lower-level headers
A proper content structure will enhance both text readability and SEO. Remember to divide your paragraphs with H2 headers containing keywords. It will increase keyword density and point the robots to the most important phrases discussed in the text. Use the H3 headers as well. They will allow you to prepare a practical table of contents that you may present at the top of the article – just like we did ????.
Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions may not be a direct ranking factor for your website and affect your promotion more than your position in Google. Still, try to write them using your main keywords relevant to the particular page. If you do, users who type a keyword-related query will see that keyword in bold in the search results, which may improve clickability of your listing. Then, Google may interpret the larger number of clicks as a signal that your website has value and eventually raise its rank.
Keywords
Keywords are one of the most important ranking factors in Google. They are essential for properly building up website visibility in the search engine. Around 1.3–2 billion keywords get entered in Google every day. That’s what allows users to find your website. For years, the algorithms have worked to adjust the search results to the user intention in the best possible way. That is why when you enter a phrase in Google, you get a list of sites that best respond to your query. When you prepare your content, make sure to read up on Keyword Density, Topical Authority, and Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI).
Keyword Density – the level of keyword saturation across the content. Generally used to denote the number of times a particular keyword appears on a selected page. Keyword density may be calculated for keywords in the inflected forms (plurals, past tense) or the main form only.
Topical Authority – the depth of the expertise presented across the website. To achieve it, focus on exploring many topics within one main category. For instance, instead of describing all the diets you know in one long article, split your content into parts: the Dukan diet, the ketogenic diet, the paleo diet… and provide a detailed description for each part. Websites with better depth of expertise tend to seize higher ranks in the search engine.
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) – informally referred to as semantic keywords. These keywords may be described as all the phrases that bear a thematic connection to the main keyword but aren’t its direct synonyms. An example of LSI is the following wordset: football, Robert Lewandowski, football pitch, fans, euro 2021. The SEO industry has created many publications on the topic, some of which undermine the importance of LSI. See: https://ahrefs.com/blog/lsi-keywords/.
Nevertheless, it’s certainly a good call to enrich your articles with semantically related keywords. In other words, all the keywords that may matter in the context of our text.
Google concurs:
„These relevance signals help Search algorithms assess whether a webpage contains an answer to your search query, rather than just repeating the same question. Just think: when you search for ‘dogs’, you probably don’t want a page with the word ‘dogs’ on it hundreds of times. With that in mind, algorithms assess if a page contains other relevant content beyond the keyword ‘dogs’ – such as pictures of dogs, videos or even a list of breeds. It’s important to note that, while our systems do look for these kind of quantifiable signals to assess relevance, they are not designed to analyse subjective concepts such as the viewpoint or political leaning of a page’s content.”.
If you’re looking for other inspiration sources apart from the available SEO tools, have a look at Google autocomplete results and the “Related search” box.
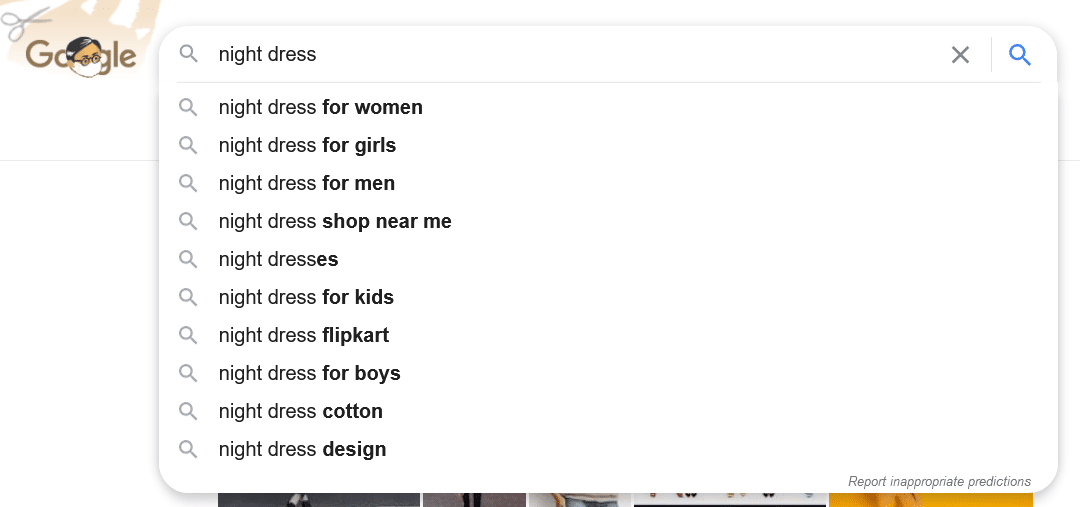
Formatting
Another point of importance is to choose formatting that improves readability – for users and search engine robots alike. A well-formatted piece of content has an introduction and conclusions, several subheaders (or more), bulleted lists, and fragments in bold. Additionally, your text may include quotes, italicized or underlined text, tables, links to other pages, or graphic elements such as multimedia or infographics. Good formatting may help you seize “position zero” in Google – the Direct Answer box. In terms of SEO, remember that subheaders work best as H2 headers featuring the most important keywords. When you want to put the key information in bold, opt for <strong></strong> tags rather than <b></b>.
Table of contents
Tables of contents are not a popular optimization technique on websites. However, adding one may make your text more useful to the user. In longer texts, a table of content facilitates navigation and saves time. That’s the two main benefits you stand to gain. With a table of contents, the user can scan through the headers without scrolling down the entire content. It’s also easier to go back to where they stopped reading.
A table of contents may also improve the visibility of your article in the browser. A clear architecture of information and internal linking to individual subheaders optimized for SEO translates into better indexing. For search engine robots, it’s a signal that they’re dealing with a website of value. It’s definitely worth it to take a look at the tables of contents provided by the biggest online encyclopedia – Wikipedia.
Internal linking
Well-planned internal linking is one of the on-site ranking factors that can significantly improve your website’s position in the search results. In-text internal linking means that within the body of your article/description, you post links to other pages of your websites. Internal links may take up various shapes but they’re most effective as the exact-match anchor texts featuring specific keywords.
An exact-match anchor text includes a particular keyword and tells the search engines that this phrase is important for the target page. A red dress is an example of an exact-match anchor text. It’s also a good idea to implement internal linking with ordinary URLs, especially if they contain keywords. In principle, an article of average length should contain no more than 5 links. Internal linking does not have to follow any specific patterns – you may link to content that’s strictly or loosely related to your article.
Content updates
Our articles quickly go out of date. They get ousted by newer, fresher content from other sites. Therefore, once in a while, it’s a good idea to give them a facelift. The easiest way to do that is to analyze the articles of our rivals, find new keywords that they are ranking for, and optimize our content accordingly. In some industries, trends change real fast, so what was all the rage a few years back may now be obsolete.
Text length
In principle, Google ranks and assesses long expert content higher than shorter articles. As people say: content is king. A longer article will contain more keywords, have better visibility, and usually provide a broader account of the topic, which will enhance its assessment from the perspective of the search engines. Let’s remember that article length is not everything – tend to other elements we discussed as well. Finally, by all means, check the average text length of your rival websites that seized the top ranks in Google. Let’s learn from the best.
Alternative text
Alt attributes are created for people with visual impairments who browse the Internet with the use of dedicated readers. If we provide alt attributes, these users will know what content features in a given photo or a graphic. Alt attributes have also added value for search engine robots, which use them to better understand the context of the text and the image.
Besides, the alts matter for SEO. Nowadays, site visits from Google Images may add up to some ten to twenty per cent of your total traffic. Adding alt attributes raises the chances that your clients will find you there. Additionally, if your alternative text includes your target keywords for the relevant page, you’re giving a (slight) boost to your Google rank.
Wrap-up
If you’ve made it to the end, you know which content optimization methods will work for your website. Now you can start generating hundreds of unique views, outdo your competition, and become an industry leader. SEO copywriting will work for e-commerce businesses, company websites, content portals, and all sites aiming to increase their organic traffic from search engines.
Remember that content creation according to the rules of SEO copywriting should always start with a meticulous analysis of keywords, which – when properly executed – is at least the half of success in building up your website visibility. Besides, follow the guidelines on the optimization of elements that have the largest impact on SEO and are described as the key ranking factors. Without SEO support, even the perfect content of top value will be lost in Google among hundreds of others which compete for high ranks every day.
 Klaudia Hadała
Klaudia Hadała  Robert Gąsior
Robert Gąsior