Internal linking is certainly one of the most important elements of SEO and also the foundation of a website, which has a key impact on its visibility in search engines. In this article, you will learn the best practices and strategies for internal linking.
What is internal linking?
.
Internal links are placed in the HTML code of hyperlinks that lead to other pages on the same domain. Almost every site has them, but the owners of most of them do not realize the important function they perform.
A hyperlink consists of a URL address, which is placed in the <a> tag as the value of the href attribute, and an anchor, or so-called link content, placed between the <a> tags of the HTML code. The link between the <a> tags then displays in a fixed form – it can be text or a pure URL.
Example:
<a href="https://domena.pl>Anchor Text</a>
.
An internal link can be placed on the site in two ways – as an address with a relative or absolute path.
A relative path, otherwise known as a relative path, is one in which there is no need to include the full URL of the page you want to link to.
It looks like this, for example:
/category-X/product.html
This is a link to a product, located on the site in category X, which in turn is located in the main directory of the domain. The default base folder in the relative address is the main address of the site, e.g. https://domena.pl.
In contrast, an absolute path, otherwise known as an absolute path, presents itself as follows:
https://domena.pl/kategoria-X/produkt.html
This is the full URL, along with the name of the protocol (whose inclusion in the absolute path is necessary).
There is no clear answer as to which links (relative or absolute) are better in terms of SEO. Both options have their advantages. Building a website based on relative links is more advantageous when, for example, moving the site to a different server, changing the domain or migrating to an HTTPS version. Relative links greatly speed up the process of restarting the site after such changes.
As for absolute links, there is a theory that they make the job of indexing robots easier – they are given a ready-made URL to go to, without having to do the extra work of compiling the relative address with domain address.
What is the difference between internal linking and external linking?
.
It has been known for a long time that acquiring external links is a key procedure in SEO efforts. Links leading to our site from other sites (especially popular ones) contribute to improving the visibility of the site in Google search results. Such a link is otherwise known as an inbound link or a backlink. An external link can be placed on another site and lead to our website, or conversely, we can be the one linking to another site.
Many people think that only backlinks are important in SEO. Nothing could be further from the truth.Internal links are also a very important element that should be taken care of. They are significant both for Google robots, moving around the site to scan and index it, and for users, who appreciate sites with a good navigation system.
An internal link, as mentioned earlier, is a link placed on a website, leading to another subpage inside the same domain. In contrast, an external link placed on a page points to a completely different site.
Read also: How to do external linking, or link building?.
External linking in a nutshell
.
Inbound links have a huge SEO impact – they are considered one of the most important factors affecting a site’s visibility in Google. A website with an external link conveys some of the so-called “power” to the site it links to – but only if the link is not marked with the nofollow attribute.
External linkingincreases brand awareness – the more backlinks a website has, the more noticeable it is, both by users and by Google. Backlinks also help increase website traffic, especially if placed on popular sites, blogs or social media.
The best way to acquire inbound links is to create high-quality content and post it on valuable portals with a link to your site. It’s also a good idea to acquire as many natural links as possible, i.e. links that are posted online by internet users, usually in the form of recommending a particular brand, product or post to other users.
Internal linking at a glance
.
Internal links also play an important role in a website and in SEO. They help create the proper structure of the site – this is beneficial for Google’s robots, which use these links to move between pages on the site, as well as for users navigating through the site. Proper site structure makes a site easy to navigate and user-friendly, which in turn contributes to reducing the rejection rate (which determines the number of sessions on a site limited to just one page) and increasing the likelihood of making a conversion.
Internal links can be placed, for example, on a blog in articles like “Top 10 products…”. Thanks to such a procedure, a user looking for information about, for example, coffee makers, can go to the page recommended in the entry of a product located in your online store.
Posting internal links to product pages, blog posts or contact forms on your site provides both users and robots with a smoother user experience.
What benefits can a website gain from internal linking
.
Internal linking has a very strong impact on a website’s SEO. The primary benefits a site can gain with a well-planned internal linking structure are improved indexing and adequate link juice flow between subpages, which in turn translates into better search engine rankings for the site.
This can also include a reduction in the aforementioned bounce rate, which, with behavioral ranking factors, can also make quite a difference in terms of SEO. Internal linking will also be a good way to combat keyword cannibalization.
Wypróbuj Senuto Suite przez 14 dni za darmo
Zacznij 14-dniowy trial za darmoSite indexing
.
Many websites face the problem of indexation. Sub-pages falling out of the index or URLs waiting indefinitely for indexation can be a consequence of poor internal linking on the site. For large portals, this problem can be more acute, especially when new subsites are created dynamically and there are many of them.
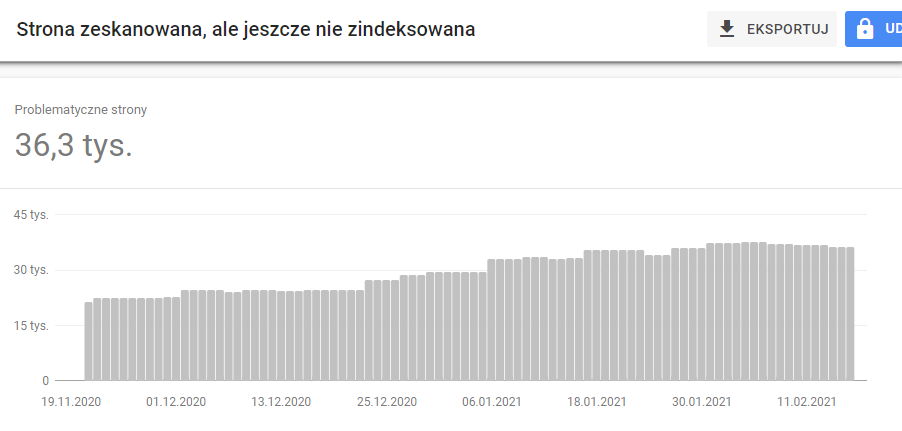
The goal of any search engine is to index as many pages on the site as possible. To index, search engines use bots that follow internal links to index more sub-pages. As you can easily guess, a sub-page that does not have any internal links or is not in the site map, or is not linked to by any external sources – will not be indexed.
Indexation problems can also be caused by a badly planned internal linking structure. Placing a sub-page too far away in the internal linking path relative to the main page can also translate into worse indexation. Therefore, it’s important to make it as easy as possible for robots to reach as many subpages on the site as possible.
Link juice flow
.
Link juice is defined asthe power transferred from the linking page to the target page. It is closely correlated with PageRank, which evaluates the authority of a website based on links leading to it from other sites. It should be noted that PageRank is distributed on a site by both external and internal links. So the better we plan internal linking on the site and direct link juice to relevant subpages, the better the SEO results will be.
Rejection rate (bounce rate)
.
The bounce rate is defined as the proportion of visits where no action was taken other than viewing one page and then leaving it. A situation in which a search engine user visits a site and after a while leaves it, returning to the organic results, can be a signal to Google that they did not find the information they were looking for on the site – and therefore the site did not meet their expectations.
Many tests show that the bounce rate affects the results in the SERPs, so it is worth enriching our site with internal linking, which will help keep the user on the site for longer and persuade him to visit more pages.
Cannibalization
.
Failure to use the same anchors in internal linking to different subpages will sooner or later cause cannibalization problems. This is when a minimum of two sub-pages start competing with each other for search engine position. A well-planned internal linking structure can effectively solve this problem.
Types of internal links
.
To create a proper internal link structure, you need to do it well and with your head. It is not enough to place a random number of links in arbitrary places on the site and wait for results. Internal linking must be well thought out. Here are some tips:
.
Already at the stage of building the site and creating the menu, it is worth thinking about the proper use of internal linking – especially since it is mostly visible on all subpages of the site.
Internal linking in the midtext
.
This is nothing more than placing links in the content on the site, such as category descriptions and product descriptions, descriptions of individual sections on the site or blog posts, etc. This type of link can be placed in several ways. The most popular is to use anchor text, i.e. the content (the so-called anchor) under which the link is placed. This can be:
- Keyword, chosen for the linked page, e.g. “winter boots” for a category subpage with such products.
- Brand name – most often under such an anchor is the address to the main page of the site.
- Title of a given subpage – for example, when linking to a blog article, we can use its title and insert a link under it.
- The so-called Zero Match – that is, a word that does not in any way match the linked sub-page, but indicating that there is a link under it, such as “Here”. – This type of internal links is better not to overuse, because they do not provide Google robots with any information about the content of the linked page.
- We can also put a link in the content in the form of a pure URL, such as “Take a look at https://domena.pl/ to learn….”.
.
.
A way that is also worth using is to place links under graphics, e.g. in an article on interior design, it is worth placing photos under which you can place links to the products in them.
It is worth implementing linking in the content, especially on the homepage and include links to the most relevant subpages. However, this should be done in moderation. For blog posts, it is a good idea to cite your previous articles and link to them from a specific key phrase.
.
Breadcrumbs, or path menus, form the basis of site navigation and show where a user is. KEach item included in the breadcrumbs menu provides an additional internal link to key pages on the site.
.
The footer is the space at the bottom of the page. It would seem to be an unimportant element, but nevertheless this is not true. Users very often look there for information, for example, about the company, so it is worth taking advantage of this and implement internal linking to the most relevant subpages of the site.
Internal linking from product pages
.
In the case of an online store, it is worth implementing, for example, the module “users who bought this product also bought” or “similar products”. This is a very good way to expand internal linking and encourage users to buy more items from the store.
Internal linking from site map
.
It is recommended that the site has a so-called site map (site map), which contains URLs to all possible sub-sites.
Internal linking from graphics
.
It’s worth knowing that search engines use the text in the alt and title tags of a given graphic to understand what’s on it. When linking internally from graphics, use alternative descriptions. These are texts with which to indicate to robots what is in a given image. Responsible for no alt=””parameter in the <img> tag. Descriptions should be completed concisely, taking into account what is in the image. The use of the “title” attribute in the tag is also recommended.
Example:
<a href="https://domena.pl/kategoria/produkt"><img src = "product-xyz.jpg" alt = "product name or key phrase" title="title of graphic" /> </a>
.
How to build a correct internal link structure on the site?
.
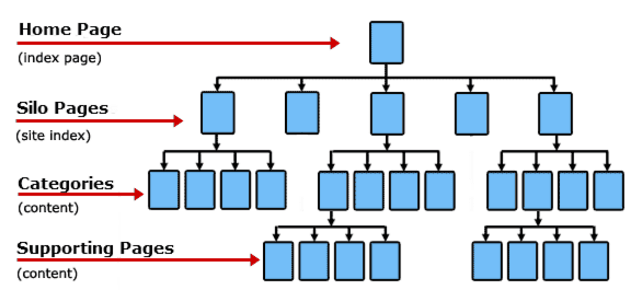
When planning internal linking, it’s best to imagine a pyramid, where the top of the pyramid is the home page, and below that are placed the next most important sub-pages in the hierarchy, until the base of the pyramid.
A properly planned internal linking structure should also be based on silos, or thematic groups. For example, if an online store contains main categories with sweatshirts, jackets and pants, we should focus on linking lower-ranking categories and products within a given silo, e.g. in the case of pants it would be chinos, sweatpants, smart.
We should not link between different silos, as this is not in line with the concept of topical auhority.
 .
.
So what elements in internal linking should be taken care of?
.
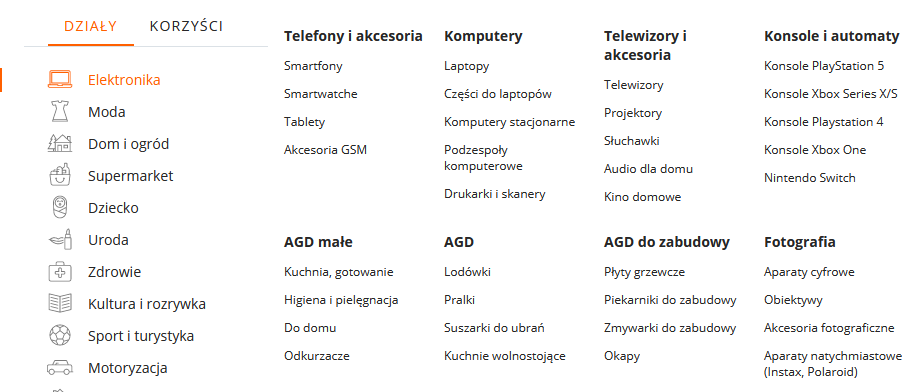
This is one of the most important elements of internal linking. The Main menu is where we should include links to all the key subpages on the site. It is also very important to use text anchors with sales keywords. An example of well-designed internal linking in the menu is Allegro, for example.
 .
.
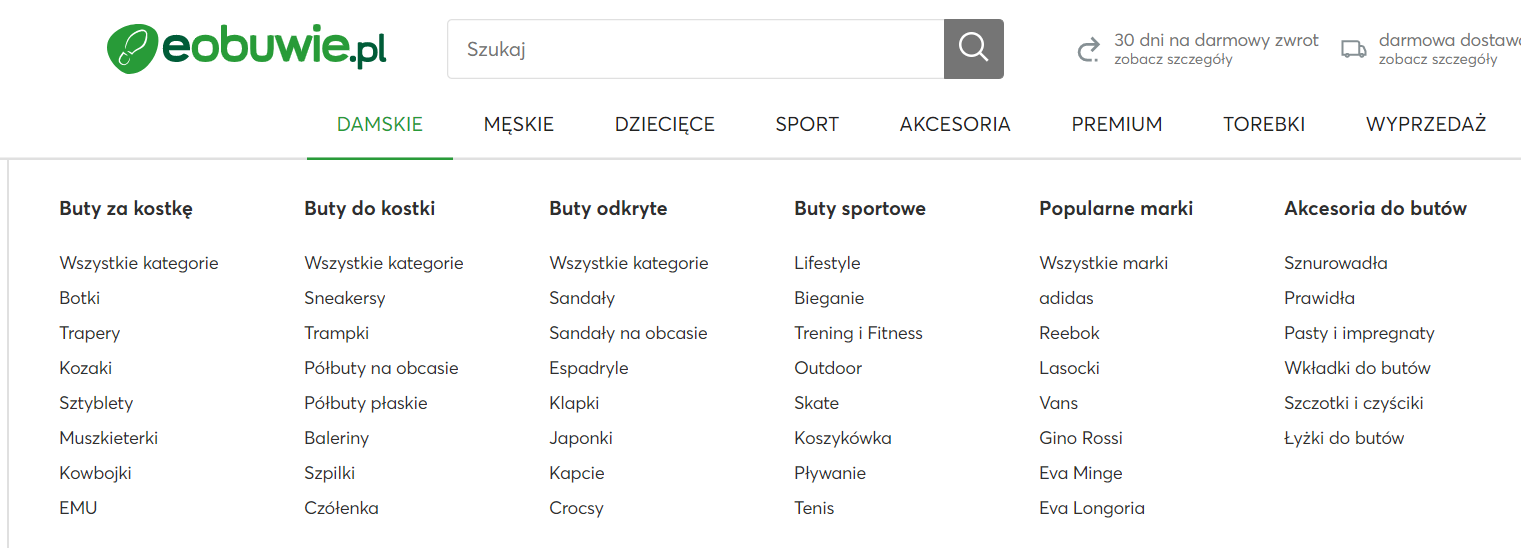
First of all, you should pay attention to how you name each menu item. It is a good idea to use in naming keywords for the particular sub-page to which you are directing from the menu. This is especially important for very large sites.
Example:
 .
.
It’s also a good idea to include a side menu on your site – which provides an additional opportunity for internal links.
Breadcrumbs
.
The aforementioned path menu. It forms the basis of the site’s navigation, showing where the user is. It helps search engine robots better understand the structure of the site. As a rule, the links in the breadcrumbs menu should be the same as the category names and at the same time contain SEO-selected keywords. All elements of this menu, except the last one, should be links and refer to particular existing places on the site..
Example:

Site maps
.
An additional element that aids internal linking is a sitemap. A sitemap is a sort of table of contents of the links on the site. It is designed to facilitate indexing of the site. It can be created in XML / HTML format. Absolutely remember to add the sitemap to Google Search Console.
Pagination
.
Proper page indexing can also be greatly affected by pagination. While for small sites standard pagination link building should suffice, for larger portals properly designed and implemented pagination can significantly improve site indexation.
You should certainly pay attention to,whether the robots from each of the subpages will have access to the first and last pages. Keep in mind the back/forward links. In the case of a very large number of subpages, it is also worth thinking about midpoints in pagination, which will provide additional links that will shorten the path for a search engine robot to reach many subpages at once.
Anchors
.
When planning internal linking, do a keyword analysis beforehand and select those with the best search potential. Then use them when creating text anchors in internal links.
It is worth noting the use of anchors like “read more”. They are very often used for blog posts. A much better option will be to leave the title of the entry itself, which will also be a link leading to it.
Linking from content
.
When we publish a blog post, it is worth planning in advance what other thematic posts it will link to. Admittedly, there is no rigid rule here as to the number of internal links, but the number of 3-5 links per average length article will be optimal here. You should also stick to topic groups (silos).
Nofollow
.
As a rule, nofollow attributes should not be used in internal linking, except for some exceptions, such as links with filtering or sorting parameters or the site’s terms of service and privacy policy. Therefore,if you don’t have a valid reason to use them, don’t do it. You certainly won’t seal the linkjuice flow this way.
Number of internal links
.
According to Google’s first recommendations on the maximum number of outbound links from a single page, which appeared on a blog for webmasters, it should not be more than 100. Google’s current documentation even talks about several thousand links as the maximum reasonable number of internal links found on a single page.
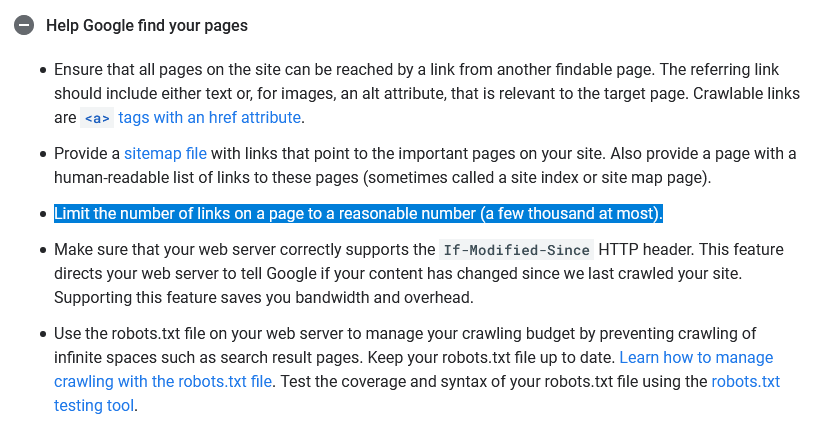
Regardless of the type of site, the first recommendation will be much more effective for SEO than the one that says several thousand links.
Link depth
.
The 3-click rule has its justification. We should not hide sub-pages deep in the site that would be accessed only after 10 clicks, starting from the home page. While it is obvious that the number of clicks will vary depending on the type of site, every website owner should plan its architecture in such a way that the depth of the last click is as low as possible, taking into account the business goals.
Frequently made mistakes in internal linking
.
Some of the most common mistakes encountered in internal linking include:
- lack of sales anchors,
- linking to non-existent subpages,
- too many links on one subpage,
- use of anchors like “read more”,
- frequent linking to subpages from different topic groups (silos),
- repeating internal links in the content, directing to the same subpages,
- linking to irrelevant subpages,
- orphaned pages with no internal links leading to them,
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Every once in a while, it’s a good idea to conduct an audit of existing internal links, especially if we plan to implement more. In this way, we can verify if there are problems with internal linking on the site. First of all, you should check:
Damaged internal links
.
These are internal links that lead to non-existent resources on the site. These can be forgotten links, such as in articles or to product pages that are no longer available. If there are links on the site pointing to a broken URL, this is usually a situation that needs to be resolved.
Links to such addresses should be replaced with correct page addresses, and the existing erroneous addresses should be 301 redirected to the most relevant subpages. Otherwise, such a situation may adversely affect the usability of the site, with SEO implications.
Orphaned pages
.
Orphaned pages are pages with no internal links. These pages are mostly not indexed and it is very difficult to get to them. In order for indexing robots to find any page, it must be sub-linked. It may be the case that orphaned pages represent lost potential to get a lot of traffic to your site, but you don’t realize that they are orphaned. So it’s worth doing a site audit to see if there are any “orphaned pages” inside the site and lead links to them.
Linking to subpages with redirects
.
All links within the site should direct directly to the resource, without calling 3XX redirects along the way. The idea here is to avoid creating so-called redirect chains – it could lead to wasted crawl budget when Google scans a page linking to another subpage that is redirected to yet another.
Too many internal links on a page
.
You should avoid putting too many links on the page. First of all, it does not look attractive and makes it difficult for users to navigate the site, and secondly, Google may treat it as spam.
Inappropriate selection of key phrases for internal linking
.
In order for internal linking on the site to make sense, you need to think very carefully about its structure beforehand. First of all, you should choose the right key phrases for each sub-page of the site and link to them according to the accepted scheme. Moreover, when choosing phrases for internal linking, it is better to avoid phrases that are too general, such as “for kids”, “sports”, “women”, and choose those that are more specific or with long tail, such as “winter boots for kids”, “sports jackets”, “clothing for women”.
.
Internal link analysis tools
.
Here are the tools you should use to analyze and check internal links.
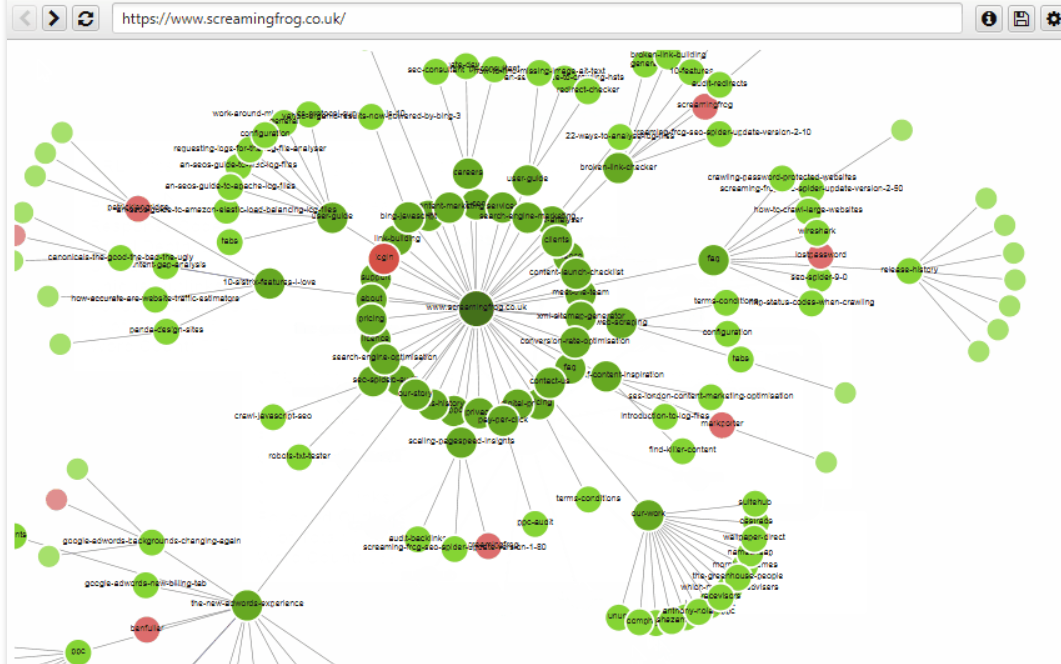
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
.
Screaming Frog is a robust web crawler that allows you to thoroughly examine your site and check its most important elements. Among other things, the tool informs you about non-functioning links on the site. The data is presented in both tables and charts. They greatly facilitate the analysis of site architecture and internal linking.
Sitebulb
.
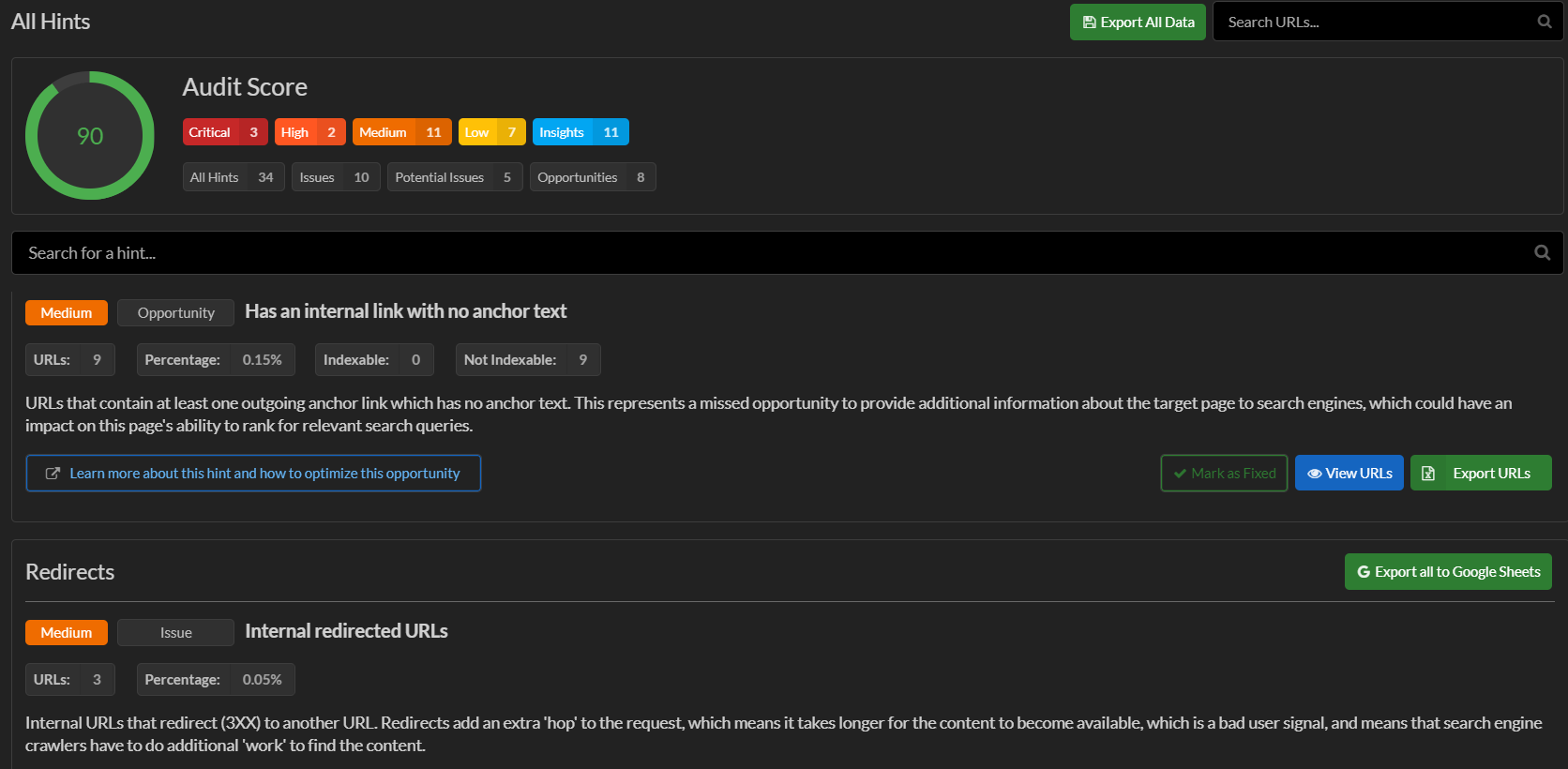
In the Sitebulb tool (which is also an advanced crawler) we have the ability to check for possible internal linking errors on the site. The data in the program is presented on colorful graphs, which makes it easy to analyze. We also get ready-made hints about the errors and, of course, the specific URLs in our site that are affected.
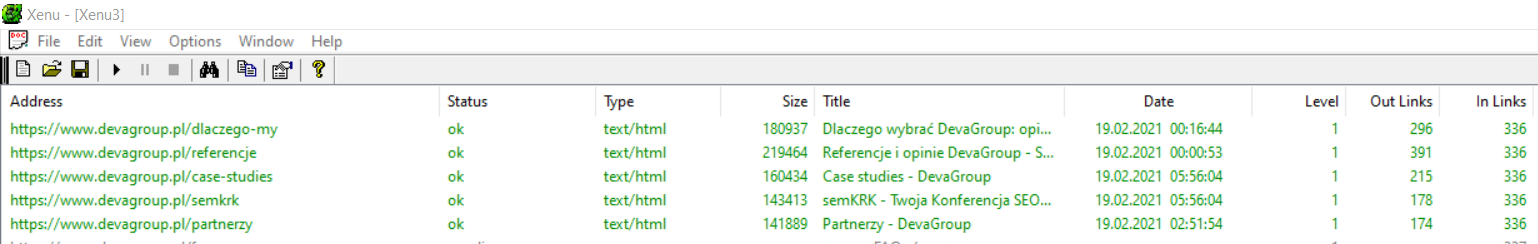
Xenu’s Link Sleuth
.
Xenu’s Link Sleuth program is a simple crawler that scans the site, creates a map of the site’s links and presents us with key information so that we can catch possible technical problems. By providing us with a list of all internal and outbound links, the tool allows us to detect non-functioning, broken URLs. The tool is free and features a simple interface.
WildShark SEO Spider
.
WildShark SEO Spider is a free tool that presents us with a list of all website URLs and detects errors and broken links. The data is placed in separate tabs, such as Internal URLs, External URLs, Broken links, etc. The tool is ideal for reviewing the general state of a site, but may not be sufficient for advanced analysis.
Visual SEO Studio
.
Visual SEO Studio is a tool that allows you to analyze your pages in detail, providing you with ready-made reports about problems on your site, a list of URLs and internal links. The free version of the tool allows you to crawl 500 URLs.
Broken Link Checker for WordPress
.
For owners of sites on WordPress, the Broken Link Checker plugin is the ideal solution, monitoring all internal and external links and showing which ones are broken. What’s more, broken links can be edited directly from the plugin, without having to manually update posts.
Can you get a penalty from Google for internal linking?
.
According to the official position of Google’s Gary Illyes, presented during the AMA on Reddit, you cannot receive a penalty for internal linking.

Gary Illyes: “No, you can abuse your internal links as much as you want AFAIK.”.
Note, however, the addendum AFAIK (as far as I know, that is) at the end of the sentence, which is a sort of gateway. Since Google’s search engine algorithms are now very advanced, you can’t be 100% sure that spamming internal links won’t bring an algorithmic penalty, so approach it with reason.
Summary
.
Many websites ignore the issue of internal linking by which they miss out on a huge potential for increased visibility and organic traffic in search engines. It is important to stick to the basics of site architecture, anchor texts used, depth and number of internal links posted. A site that is well optimized in this regard is sure to gain SEO profits in the form of more traffic.
 Robert Gąsior
Robert Gąsior