If you want your content to become visible in search results, it must first be indexed. So see what domain indexing is all about! In this text we also suggest how to check and improve this process.
What does the indexing of a site consist in?
.
Page indexing is the process by which Google (or other search engines) crawls the Internet to find new or updated content, which is then added to an index (a.k.a. a massive database).
The entire process can be depicted as follows:.
- Crawling-another important stage in which a web spider (called Googlebot) crawls the content of a website. The crawler analyzes the content on the pages it finds and, with the help of the hyperlinks on them, goes to the next sub-pages.
- Indexation -when new or updated content is fully analyzed, Google moves it to its index.
- Search -when Google’s search engine returns an answer to a user’s query, it relies on the content collected in the index to do so.
How to check if a page is indexed?
.
There are 2 main ways to quickly determine whether a site has been indexed..
1. Site:
.
OThe “site:” operator causes a web search engine to narrow the answers to only the address shown after the colon..
Note – remember not to put a space after the colon .
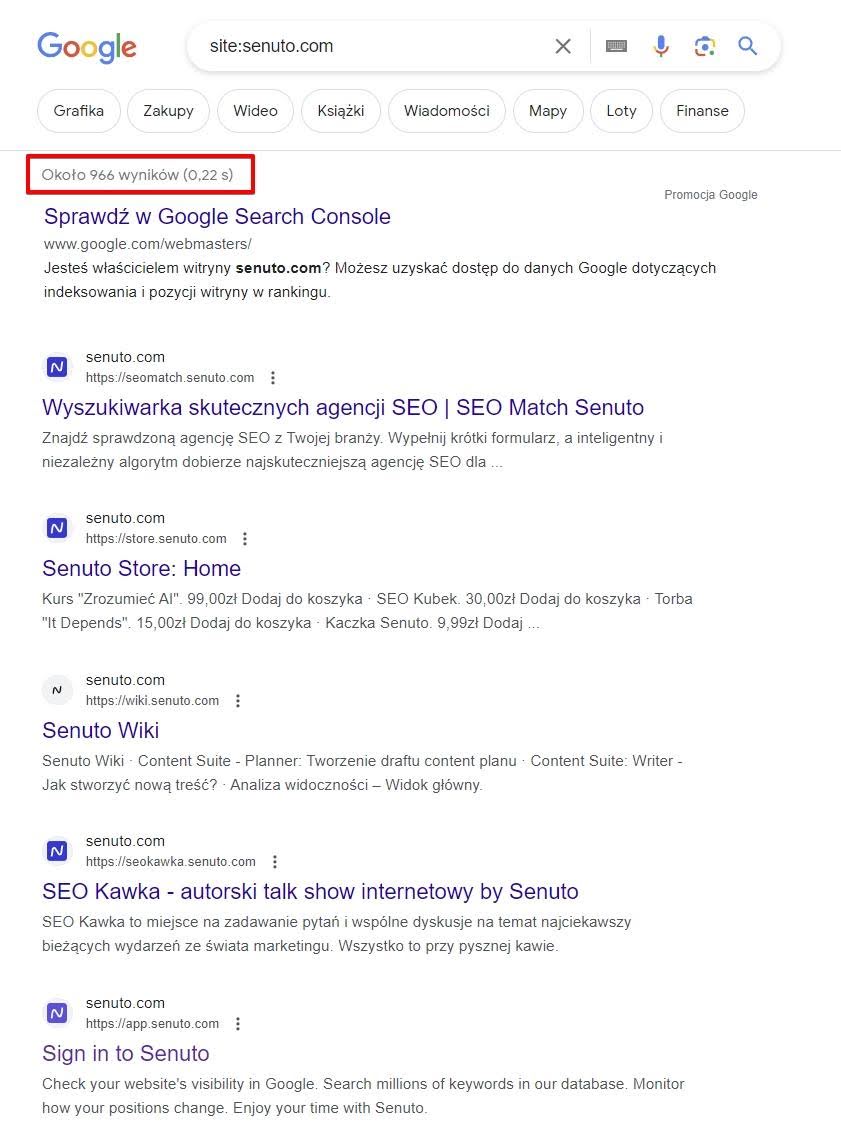
This way you can initially check if the site is indexed at all. As you can see, Google indexes about 966 different pages on the Senuto site..
However, how do you determine whether, for example, a recently published blog article is already visible in Google? All you need to do is to specify the exact address after the site operator:.
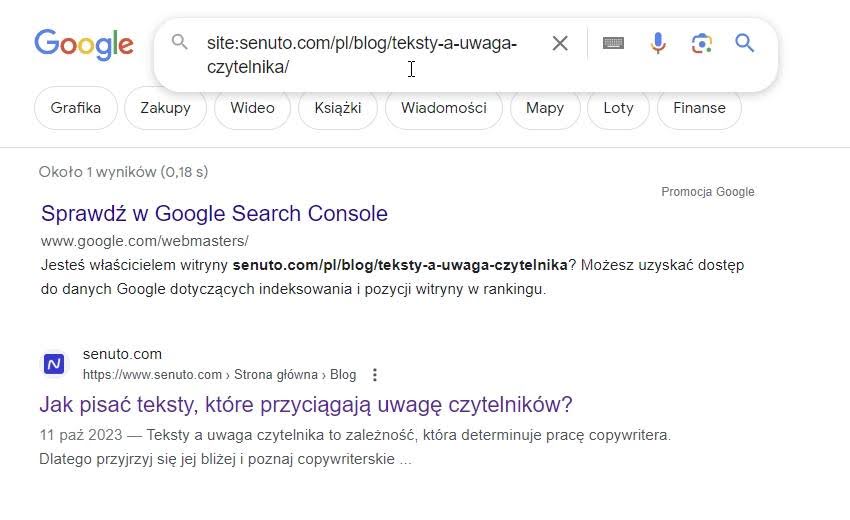 .
.
The above article is indexed by Google..
2nd GSC
.
Google Search Console (GSC) is a tool for webmasters that allows you to closely monitor the indexation status of your site.
For this purpose, follow these steps:.
- In the navigation menu, go to Index > Status.
- You will be shown a section with the number of sub-pages that have been indexed by Google.
- If the number is very small or even 0, it indicates indexing problems.
- If you want to check the indexing status of a selected subpage, enter its URL in the top search bar.
- If Google does not recognize the page, a message will appear “The URL is not found in Google”.
.
.
.
.
Good practices to speed up site indexation
.
Efficient indexing of your site’s content is not a matter of chance. Let’s take a closer look at the various ways to help with this..
1. Check the robots.txt file
.
The robots.txt text file tells search engine robots which sections of a page can be crawled. As you may have guessed, the instructions contained there have a big impact on indexing. Here is the most important information about it:.
- User-agent – with this section you can specify which bot the directive refers to. For example, “user-agent: Googlebot” will make the instructions apply to all Googlebots.
- Disallow/allow – commands allow you to specify whether web spiders have access to given content. This will allow you to block irrelevant content (such as privacy policies) so that they focus on more important content. However, if you’re not careful, you’ll prevent literally the entire website from being indexed. That’s why it’s worth taking care of proper configuration.
- Crawl-delay directive-This directive instructs robots to keep a certain amount of time between requests sent to the server. This can be helpful in reducing load, but is also capable of slowing down indexing.
designations.
The “noindex” and “canonical” meta tags are located in the <head> section of the HTML document. They have important uses in the operation of the page.
The tag “noindex”is a clear signal to the search engine not to include a particular page in the index. Here is a sample notation:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex” />.
Influence on indexing:.
- A page with a noindex tag will not be considered by Google. This is a good way to hide irrelevant content like privacy policies, internal employee manuals or draft versions. In some situations, it is possible to improve the indexation of other content by doing this.
- Inappropriate use of the designation in question can, of course, make relevant content not analyzed by Google. Such situations occur when someone, for example, forgets to remove “noindex” after completing a draft version of a page.
The “canonical”marker is used to solve duplicate content problems. It indicates to the search engine which version of the several available is “canonical” and should be indexed and displayed in search results. Here is a sample entry:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”http://xyz.pl/preferowana-wersja-strony” />.
Influence on indexing:.
- A misused canonical tag can cause Google to ignore important pages, indexing only the indicated canonical version, even if it’s not the most representative or up-to-date content variant.
3. Create a sitemap.xml file and add it to robots.txt and GSC
.
Site mapor XML sitemap is a file that helps Google understand a site’s structure and contains information about its content that should be indexed. Even more advanced versions of sitemaps such as separate indexes for video content, image files, or news items are used for complex sites.
So how to create a sitemap file? You have 3 options to choose from:
- Manually – the most difficult method, which, however, gives you great control over every aspect.
- Plugins – every popular CMS includes some sort of sitemap generation tool, such as XML Sitemap Generator for Googlefor WordPress.
- External tools – work regardless of what CMS you use, such as XML-Sitemaps.
.
How to add a sitemap to robots.txt? Follow these steps:
- Make sure the sitemap is on the server, for example, at https://www.xyz.pl/sitemap.xml.
- Open the robots.txt file.
- Add a pointer to the file. To do this, post the line: sitemap: https://xyz.pl/sitemap.xml.
- Save the changes to the robots.txt file and upload it to the server in the site’s root directory.
.
.
.
.
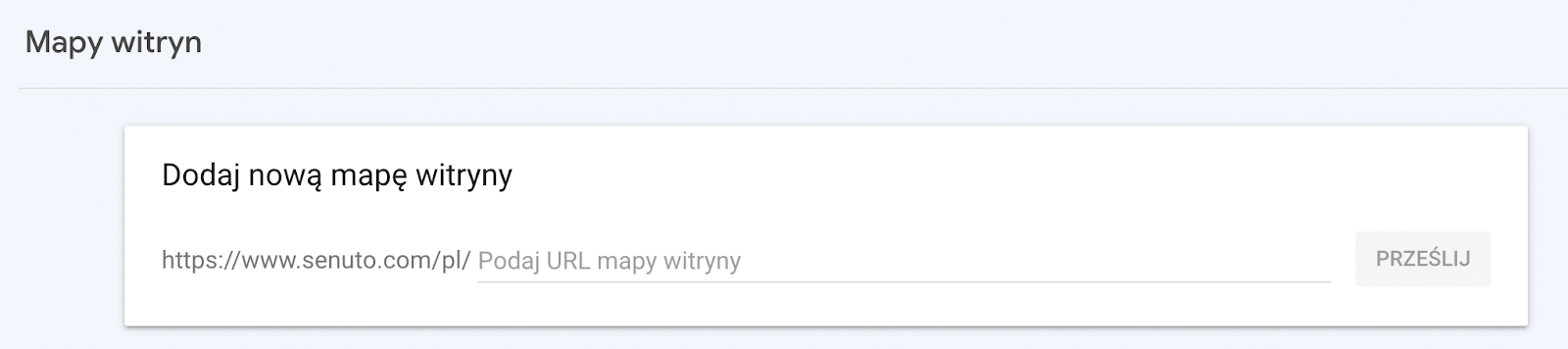
How to add a sitemap to GSC? To do so, follow these steps:
- In Google Search Console, go to Index > Site Maps.
- In the “Add New Site Map” enter its address (e.g. https://www.xyz.pl/sitemap.xml).
- Click “Submit”.
- After you add a sitemap, you can monitor its status in Google Search Console.
.
.
.
.
4. Manual indexing
.
If you are particularly anxious to index any of your pages, it is possible to speed up the process to some extent. To do so, follow these steps:
- As we mentioned earlier, if you want to check the indexing status of a selected subpage, in the top search bar of Google Search Console enter its URL.
- If the page has not been updated or indexed, click “Request indexing”.
.
According to Googlethe process in question takes several days to several weeks. In addition, the search engine developers advise:.
Remember that there is a limit to the number of individual URLs that can be submitted, and submitting multiple requests to re-index the same URL will not speed up indexing.
5. Take advantage of indexers
.
Indexers are third-party sites (usually operated by SEO specialists) that help your site be indexed faster by search engines. They work in 2 main ways:.
- Automatic link generation – linking increases the quality of a given page from Google’s point of view and increases the chance that it will be noticed in the crawling and indexing process.
- Reporting an address to search engines – using methods such as search engine APIs, HTTP requests, or RSS feeds, indexers notify Google that a given page exists.
This method can be very useful. However, remember to use it judiciously, so that such actions are not interpreted as Black Hat SEO. .
How to check the progress of site indexation?
.
Indexation progress is best monitored using Google Search Console by following the “Indexing” report.You’ll find information about indexing errors, warnings, and successfully indexed pages.
In addition, it is worth using Senuto, and more specifically the “Monitoring”and the “Pages” report..
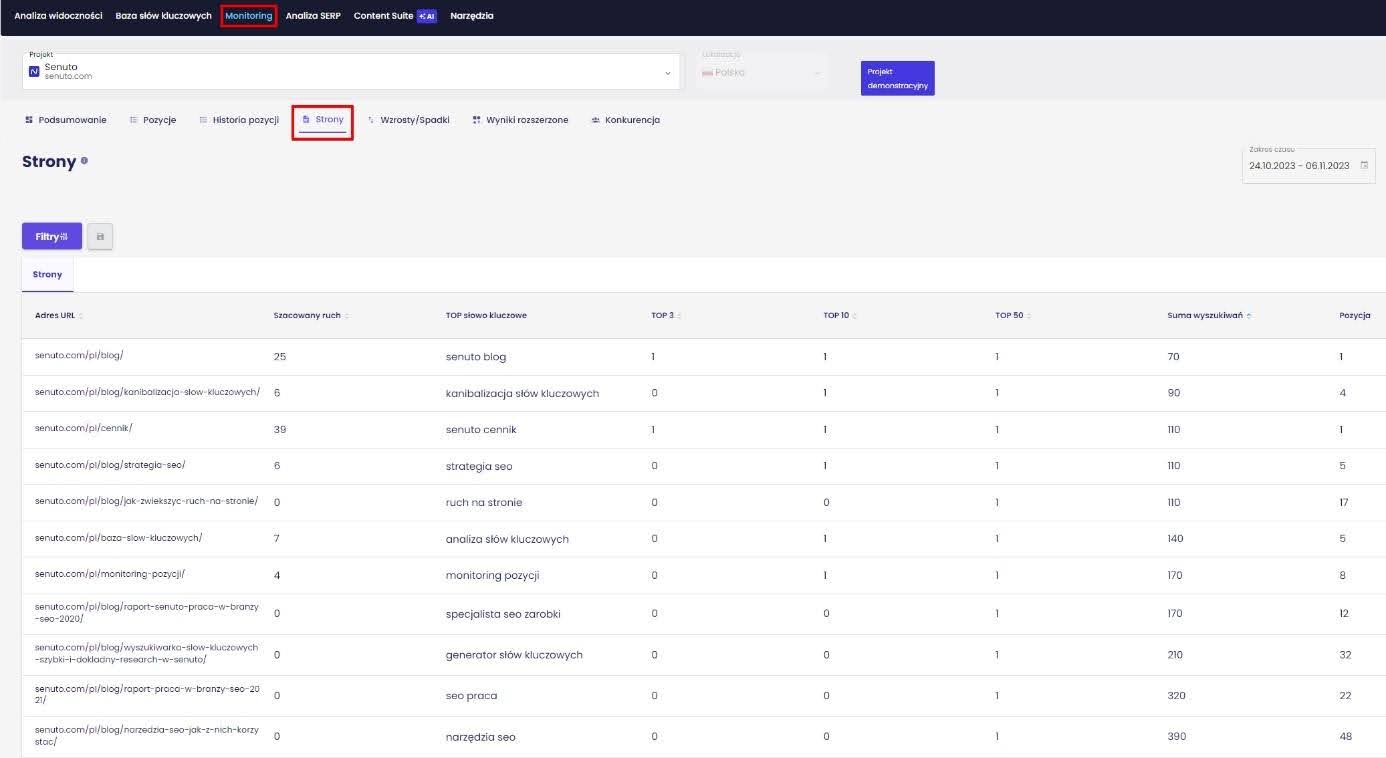
This way you can not only quickly check if the sites are visible in Google, but also how many searches they are generating and if they are positioning in the TOP for any keywords..
Summary
.
Indexing is a very important process for any website. Therefore, don’t leave it to chance. This will ensure that your website will have no problems getting visibility in Google..
What is indexing?
.
Indexing involves gatheringinformation about the content, key phrases, links and images found on a particular domain. This information is then stored in the database of a search engine, such as Google..
Is it worth indexing a website?
.
Yes. Indexing is strongly related to SEO. Non-indexed pages will not appear in search results, even if they are brilliantly optimized and written according to SEO requirements. So if you care about high website rankings, make sure your site is properly indexed.
How often does Google index sites?
.
It is impossible to say specifically how often Google indexes web pages. It is generally accepted that single pages, such as new blog posts, category or product descriptions, are indexed within a few days at most. In the case of a completely new page, this time can increase. In extreme cases it can even take several weeks, but these are not common cases.
Is it possible to speed up the indexing of a website?
.
Yes. All you have to do is click the “Request indexing” button after checking a specific URL in Google Search Console.
 Iza Sykut
Iza Sykut