What is duplication of content and why should you avoid it?
Duplicate content is a situation that negatively affects how a website is viewed by search engines. What is duplicate content? This definition refers to duplicating the same or nearly identical content in one or more places on the Internet. There are many instances when such an action is not intentional but simply due to ignorance. Duplication happens inside a single website but can also refer to the repetition of content between different sites. These two cases are the basic types of duplication.
Internal duplication (content duplicated within a single domain)
Internal duplication occurs when the same content appears on different pages of the same site, in its entirety or only in fragments. This happens when a particular subpage or homepage has duplicates (caused, for example, by CMS errors, lack of proper redirects, etc.), but also when a category or product has the same description as another URL within the site. Internal duplication threatens a site’s situation on the web less than external duplication. Still, it can sometimes be just as problematic – causing, for instance, problems with indexing subpages with the same description.
External duplication (content duplicated within multiple / several domains)
External duplication occurs when content is copied from another website, but also in the opposite case and more challenging to control – when others copy content from our website. Duplication of content also occurs when the same text is shared on the website and social media of the same brand.
Why should we avoid duplicate content?
Duplication of the same content negatively affects the positioning of the site. As a consequence, we may notice a drop in organic traffic. If we are dealing with an online store, then a decrease in traffic will be inevitably associated with a decrease in sales as well. Thanks to the Panda algorithm, introduced in 2011, Google is able to evaluate valuable and original content on the site and appreciate it in the form of high SERP positions.
How can you tell if your content is being duplicated on other websites?
The uniqueness of the content can be verified through manual actions or through special tools. Sometimes, when clicking through the site, we accidentally notice similar or the same content as elsewhere on the site or competitors’ domains (for example, providing product descriptions by producers and publishing them by distributors). This can be further verified by copying a piece of text and then pasting it into a search engine. You will get even more accurate results when you enclose the given piece of content in quotation marks.
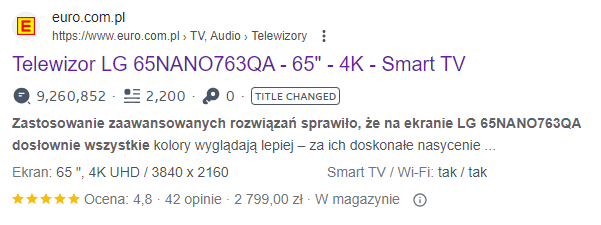
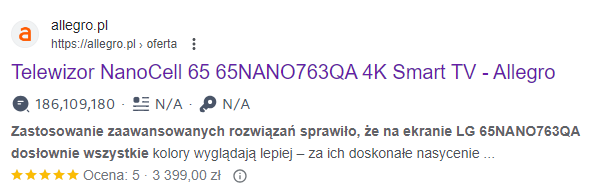
Example #1:
Product description:
https://www.euro.com.pl/telewizory-led-lcd-plazmowe/lg-65nano763qa-tv-qned-uhd-4k.bhtml
Text excerpt examined:

2 indexed results in Google with the same content:
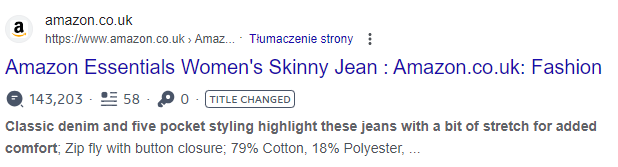
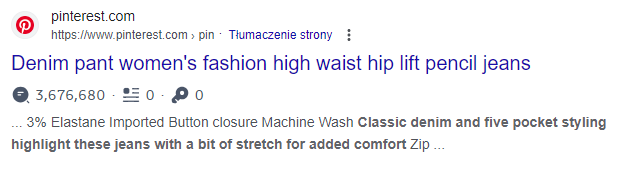
Example #2:
Product description: https://www.amazon.com/Amazon-Essentials-Womens-Skinny-Regular/dp/B07J31TT3W/
Text excerpt examined:

Many indexed results in Google with the same piece of description:
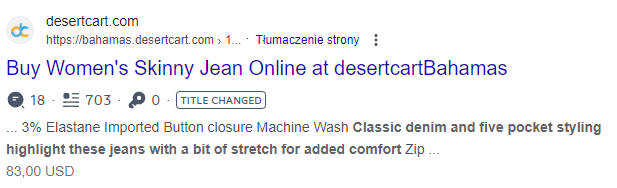
In addition to manually searching for duplicate content, which can be inconvenient on a grand scale, there are also tools to make the process easier. Such an example is Siteliner, the basic version of which already indicates a lot of useful information for website owners or SEO specialists. Here is an example of results for The New York Times site scanned by Siteliner:
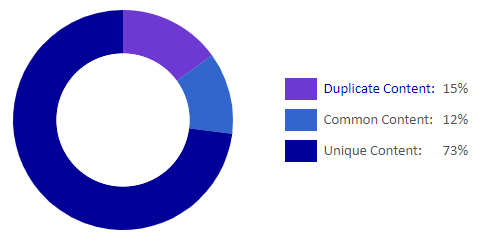
We can see that the tool indicates not only pages on which the duplicate content occurred but also the number of matching words and match percentage:
Other tools that support the process of analyzing duplicate content are, for example:
OnCrawl, where you can assign subpages in terms of similar content to corresponding clusters with a percentage breakdown. Example of visualization from the tool:
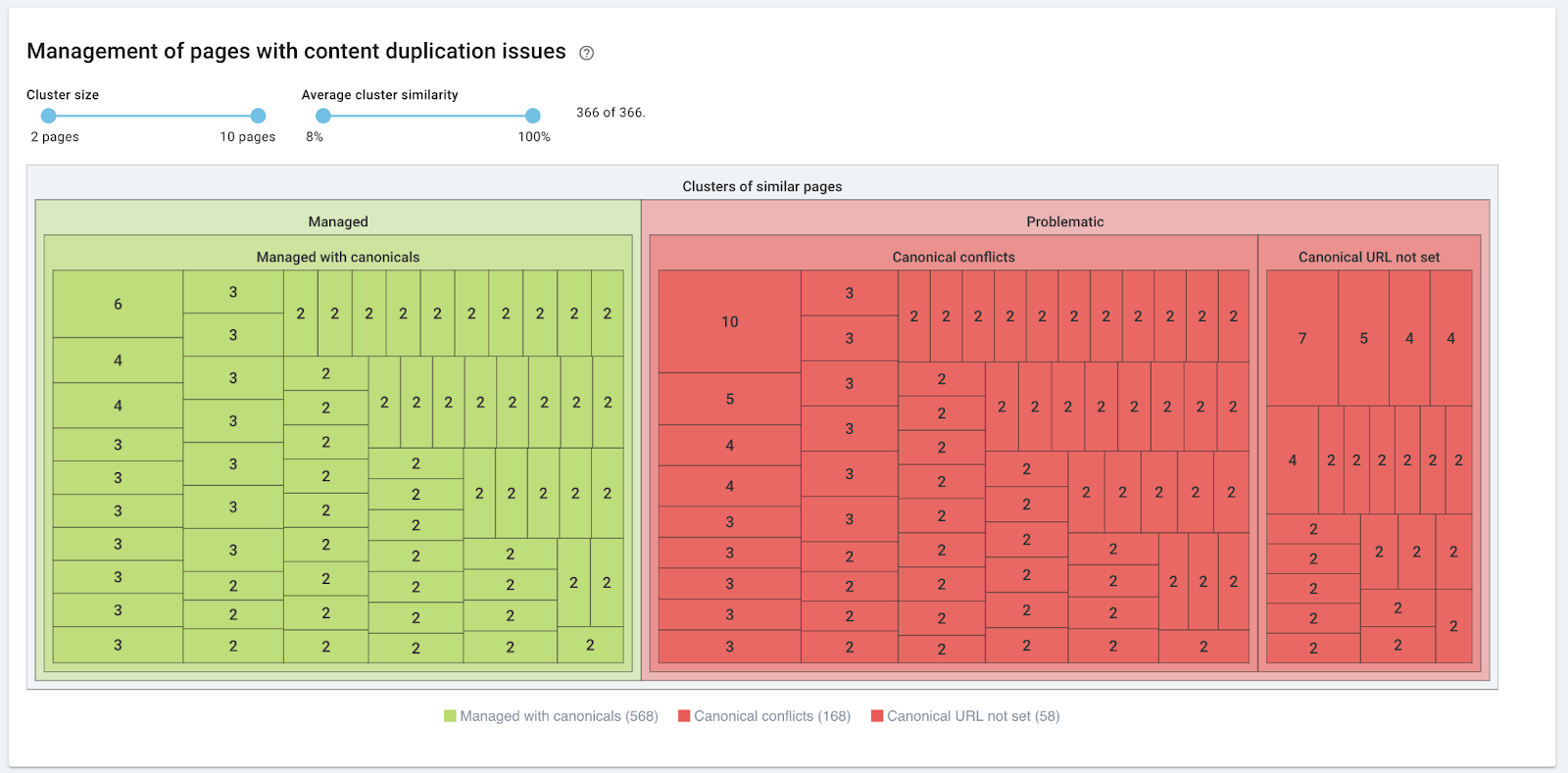
(source: https://help.oncrawl.com/en/articles/404237-duplicate-content)
- DeepCrawl (now: Lumar), which is also used to detect body, title or description duplicates;
- Copyscape – a very well-known site that helps to detect external duplication;
- Google Search Console – another tool to verify multiplied meta tags;
SEMRush – among other things, the tool depicts the status of the text’s originality with an interesting graph in its’ SEO Writing Assistant:
- Ahrefs – you can check internal duplication with this tool;
- Screaming Frog – used mainly to verify duplicated meta titles and meta descriptions;
- Sitebulb – useful to detect duplicated subpages, meta tags;
- etc.
As you can see, we can find a lot of valuable tools on the web to use regardless of your needs or budget – you just need to choose the right one for your current situation. Thanks to them, we can efficiently verify whether and to what extent our site is exposed to internal and external duplication and then counteract.
What are some common ways that people duplicate content without realizing it?
There are a lot of situations where website owners contribute to internal duplication of content. Sometimes it is due to the lack of SEO knowledge, but sometimes repetition results from errors on the page’s technical side, which are very difficult to detect at first glance. So, what are the most common ways people duplicate content on their websites?
The system of categories and tags is a common way of organizing content on a website. Sometimes website owners create categories and tags that link to the same or similar content. For example, if a page has a “health” category and a “healthy food” tag, then articles on the same topic may be listed under both. It is undoubtedly one of the most common causes of website duplicate content. Moreover, in such a situation, the so-called keyword cannibalization may also occur, i.e. in which two subpages will “fight” each other in the search results for the same keyword. On the one hand, we try to create the most user-friendly and easy-to-use website, but on the other hand, it can harm the website’s SEO. That is why when creating websites, it is essential to plan the appropriate information architecture, website structure, URL addresses and their mapping with the database of selected keywords.
Duplication of articles
Sometimes website owners may accidentally publish the same article on several pages. It can be due to various reasons, such as a bug in the CMS (Content Management System) or an oversight that the article already exists on the site, but also simply from a lack of SEO knowledge. Website owners may publish the same content on different websites to reach as many recipients as possible without realizing that these actions can contribute to the opposite effect. Some also copy and paste snippets of content from other websites without proper labelling or linking to their source. Remember that pages containing duplicate content may be pushed down in the Google results by those publishing content on the same topic but unique, which is more valuable to Google and the user.
Variable URLs
Another popular cause of content copying is using different URL variants for the same page. One of the most common situations is when a website is active under both a “www” and a non-www version or when different suffixes are used, e.g. with and without “.html” at the end of the URL. The same happens in the case of incorrectly implemented SSL protocol, which today is the basis for every website, regardless of whether it is an online store or not.
- http://domain.pl
- http://www.domain.pl
- https://domain.pl
- https://www.domain.pl
- http://domain.pl/product/product-name
- http://domain.pl/product/product-name.html
Situations when a website is active under multiple versions, making its content no longer unique, happen very often. Many website owners who do not use the support of an SEO agency/freelancer or IT team are unaware that these are entirely separate websites for Google. Fortunately, this error is usually straightforward to detect and solve since it is one of the points checked when preparing an SEO audit.
Dynamic URL generation
Some CMSs generate dynamic URLs based on parameters such as search keywords or filters. If not properly managed, they can lead to duplicate content, generating several URLs for the same article. This situation also occurs in the case of large portals and online stores, which have an extensive filter system. Incorrect filter configuration generates product listings with similar or identical content. In addition to the risk of content duplication, there is also the risk of keyword cannibalization and burning out the indexing budget. Googlebot will receive too many low-value URLs, which can lead to problems with crawling pages that are important to us.
Duplication of content on other language versions
If your website has several language versions, ensure they are created and configured correctly. Otherwise, you may accidentally duplicate your content, which happens when CMS or plugin automatically generate other versions of the page based on the primary one. What is more, sometimes website owners decide to publish the unfinished version of the website to supplement it in the future.
This action is aimed at indexing the website by Google as soon as possible, thanks to which the website will be able to start generating traffic for foreign queries. Unfortunately, that is not the case. A much better solution would be to postpone publishing a given language version and finish it before making it available online. Otherwise, we unnecessarily confuse Googlebot, which must re-index the website anyway. We also lose in the eyes of users who, for example, want to visit the website in English but come across a copy of the Polish version. Remember, the URL structure and content will also change, so what is the point?
A significant issue worth mentioning when discussing common cases of the internal copy of the content is that duplication may also apply to page elements that are not visible to the user at first glance. These are meta tags such as meta keywords, meta titles and meta descriptions. They often contain identical content reproduced on different subpages within the website. Although this content is not visible on the front end of the page, they are also considered duplicate content.
Always choose unique content
Bear in mind that duplicating content on a website can adversely affect SEO. Search engines may incorrectly index the page or consider it spam due to low-quality duplicate content. Therefore, site owners must refrain from creating identical content on various subpages and regularly check our sites for possible content copy issues using available online tools.
How can you prevent your website from being penalized by Google for duplicate content violations?
Now that we know the most common ways people duplicate content on their web without realizing it let’s discuss how to prevent it.
Create original content
The first and foremost way to avoid being penalized by Google for duplicate content is to create only original and valuable content on your website. Do not copy content from other sites. Provide unique, helpful information to your target audience. Thanks to this, you will gain in the eyes of both Google and users, who will undoubtedly appreciate the high quality of the published content. Do not duplicate content on several pages within your website. If that is the case, consider changing its layout or reorganizing your content in a way that will allow you to eliminate duplication of the same content on different subpages.
At the same time, try to avoid using auto-generated content tools or at least use them cautiously. Although AI is nowadays trendy and such tools are definitely worth testing, always remember to verify the final content, especially in terms of originality. Manual content creation is always the best approach because it allows you to provide valuable and unique information.
There are cases in which, due to the structure of a given website, subpages with very similar or identical content are generated, but you need them so they cannot be removed. If your site is facing such a problem, it is essential to use the canonical tags. Their role is to inform Googlebot which version is the main, canonical one and should be displayed in the search results. When implementing canonical tags, make sure that they are implemented correctly on all pages within the site. Incorrectly implemented can cause severe problems with the indexation of your website, which leads to the loss of valuable traffic.
Canonical tags are just one option up your sleeve for pages that search engines shouldn’t index but cannot be removed. Apart from canonical tags, another good solution could be the use of the following meta tag:
be removed. Apart from canonical tags, another good solution could be the use of the following meta tag:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, nofollow”>.
Adding it to the pages will block their indexation in Google search results, thanks to which blocked pages will be available within the website, but they will not cause duplication of content. Remember, though, that the lack of indexation means these pages will not generate any traffic on the site. As with canonical meta tags, noindex meta tags should be implemented carefully so you don’t block landing pages that generate valuable traffic to your site.
Monitor your website
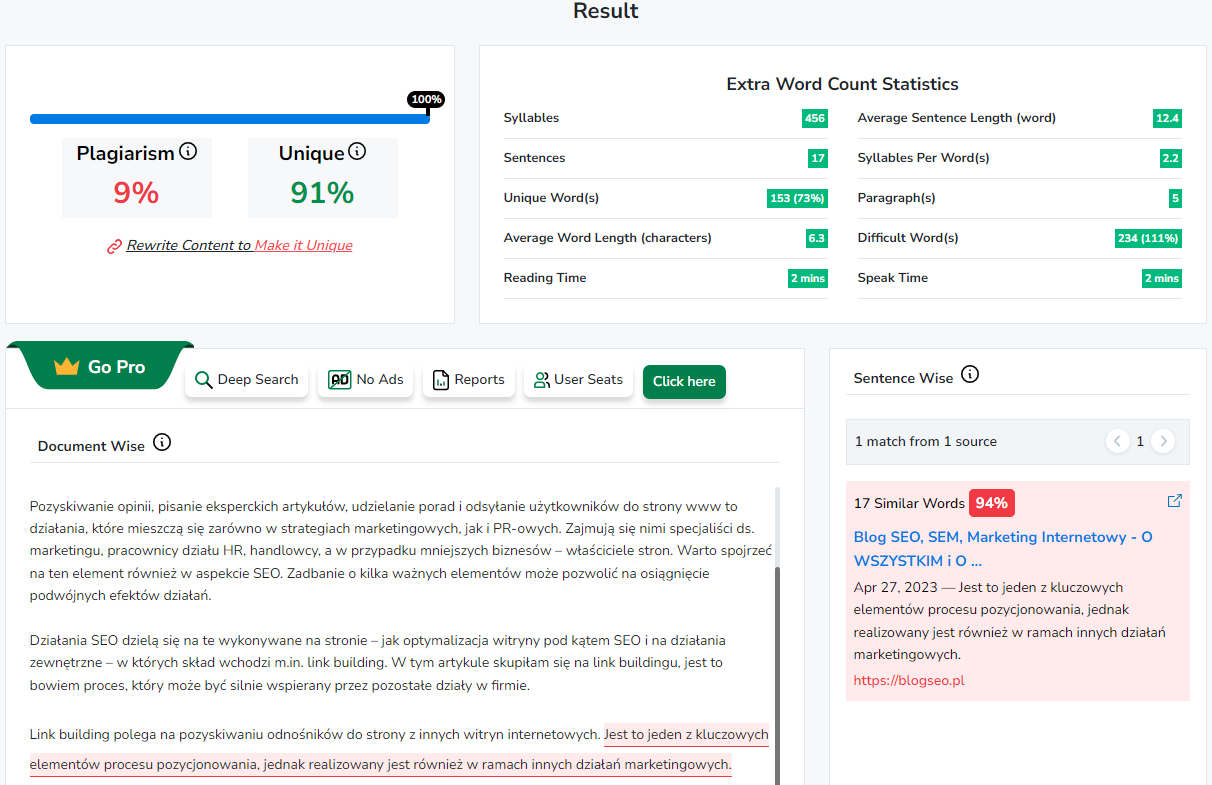
Remember to monitor your website for potential duplicate content regularly. There are many valuable tools that you can use to see if your content is duplicated, which are extremely helpful. We can quickly check whether our content is unique. Moreover, if not, we get specific links to the sites that copied them.
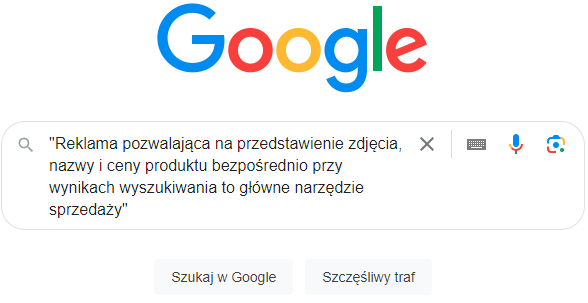
Another way to check the uniqueness of our content, though more time-consuming, is to copy and paste a random part of the description from our website in quotes into the Google search engine. The search engine will return a list of all indexed results containing the given description:
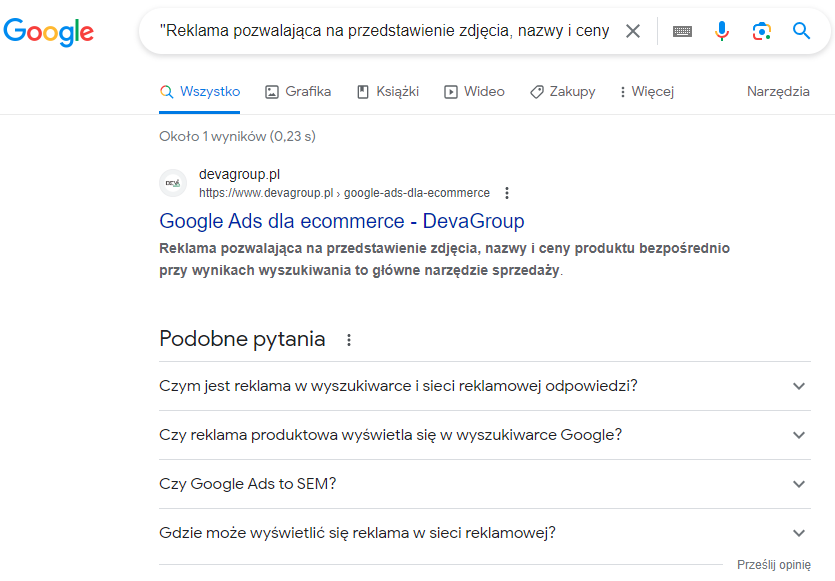
Regularly review and analyze your website’s content to check for accidental internal duplicates and intentional external ones. Focus mainly on the highest-value pages that generate the most organic traffic.
Improve the page structure
Take care of a clear and logical structure of the website. Ensure your page has a hierarchy where content is grouped into appropriate categories and subcategories. It will help you avoid creating unnecessary subpages and duplicating content about which you may not even know.
Appropriate and well-thought-out information architecture is the key to creating a website that will be easy to use for the user but also SEO-friendly. Implement a thoughtful internal linking strategy to highlight relevant and related content to the user and the Google crawler. In this way, you will help search engines understand the hierarchy and value of individual pages and avoid seeing them as duplicates.
Consult an SEO professional
If you are still determining what steps to take to avoid being penalized by Google for duplicate content, it is worth consulting an experienced SEO specialist or SEO agency. This type of help in the form of a one-time consultation or ongoing support will help you identify and fix duplicate content issues on your site. In addition to identifying problematic places on your website in terms of duplicate content and the solution, you will also receive useful tips on preparing your content well for SEO.
What are some other things to consider when creating unique, original content for your website or blog?
Some of the issues surrounding internal and external duplication that are worth taking care of when creating content are listed below. Check out how the situation presents itself on your site:
- Keyword Selection: Conduct keyword research to find out what are popular search phrases in your industry. Use these queries in your content to increase your site’s visibility in search results. Select keywords and synonyms that are actually searched by your audience and monitor them to update your strategy if needed. Make sure that keyword cannibalisation doesn’t occur within your website.
- Quality content and its relevance: Create valuable and unique content that is useful to readers. Visitors are the ones that determine if your content is good. Make sure your site’s content is relevant to your site’s themes and addresses your users’ needs and interests. Provide valuable information that is relevant to your target audience. If possible, tailor content to users’ preferences and needs. You can do this based on demographic information, user behavior or preferences expressed during interactions. Personalizing content increases user engagement and interest levels.
- Up to date content: Keeping the content up to date or trying to create evergreen text can positively affect your search engine ranking. You have to make sure from time to time that users can find the right information – this shows to Google bots that your site is relevant and still alive.
- Keyword presence: Place keywords in strategic places in your content, such as headings, first paragraph, main content and conclusion. However, remember to write naturally and fluently, and avoid oversaturation with keywords (keyword stuffing).
- Headline structure: Use a proper hierarchy of headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) in your content to clearly and logically present the structure of the article. This affects the readability of the content and helps search engines understand the hierarchy of information on the page. Avoid implementing multiple H1s or subpages without H1. Make sure your title and headlines are attractive and catch the attention of readers.
- Content structure: Create content that is well-organized and easy to read. Use appropriate headings, paragraphs, bulleted lists, bolding, tables, appropriate image files etc. to make it easy for readers to browse your content.
- Content length: Create content of appropriate length that provides comprehensive information about the topic at hand. Longer content often has more value to search engines and may be more likely to rank higher in search results but it is not a universal principle.
- Internal linking: Include internal links to other subpages on your site that are related to the content. This helps both users and search engines navigate your site and understand your site’s structure. An internal link can help a new subpage gain more visibility.
- Sitemap XML and HTML: The new content should also automatically be included in the XML and HTML sitemap (if your site has one) – this will help it rank faster in the search engine.
- External linking: Include links to credible and valuable external sources that complement the content topic. Linking to authoritative sites can positively affect ranking in search results. It is worth noting whether and which links have the “nofollow” attribute, which generally limits the link juice flowing out of the site.
- Backlinks and content distribution: Work to gain valuable and natural backlinks from other websites. Backlinks from authoritative and related sites can positively impact search engine positioning. Promote your content on various platforms such as online forums, newsgroups, guest blogs, etc. Expand your reach and reach new audiences. Network and build relationships with other sites in your industry. You can do this through guest posts, link exchanges, joint promotions or content co-creation. Mutual support can benefit both parties, including increased traffic and SEO.
- Image optimization: Add alt descriptions to images on your site to make it easier for search engines to index and understand image content. It is also important to have a properly constructed image file name that can enhance the effect of the alt description. The format of the uploaded file is significant too. Also, make sure images are properly compressed so they don’t slow down page loading.
- Page Load Speed: Optimize your site for loading speed to provide users with a fast and smooth experience. Compress files, use a cache, minimize HTTP requests and apply other optimization techniques.
- Responsiveness: Make sure your site is responsive and adapts to different devices and screen sizes. With many people using mobile devices these days, responsiveness is crucial for usability and search engine positioning.
- Fix bugs and improve usability: Regularly monitor your site for errors such as broken links, non-functioning elements, loading issues, etc. Also take care of user convenience by ensuring intuitive navigation and ease of use of your site.
- URL structure: Create user-friendly and understandable URLs that reflect the content of the site. Use relevant keywords in URLs, but avoid long and complicated strings. It’s good to know that there are official Google URL structure guidelines that should be followed.
- Meta descriptions: Customize the meta descriptions for each page to get users to click on search results. Shorten the meta description to an appropriate length, but ensure that it is attractive and contains relevant information. The preferred length of the meta description (or meta title) changes from time to time, so it is worthwhile to occasionally verify this aspect and correct it on your site. Let’s also consider the length in pixels, not just in the number of characters.
- Social Media: Promote your content on social media platforms to increase its reach. Share links to articles, blogs and other valuable content on your site to attract more visitors. It’s also worth ensuring that users can easily share the content you create. They will be able to do this, for example, by introducing share buttons.
- User interaction: Encourage user interaction on your site, such as through comments, social sharing, contact forms, etc. User activity can help build engagement and create a larger community around your site. Respond to user comments and questions to build positive interaction and increase trust in your brand.
- Data analysis: Use data analysis tools such as Google Analytics to monitor traffic to your site, understand user behavior and adjust your content strategies. Regularly monitor analytics data, such as traffic, search engine positions, conversion rates, etc. Analyze results and take optimization actions based on the information gathered. Continuous improvement and strategy adjustment are essential to stay competitive in the SEO world.
- Build authority: Create high-quality content that establishes you as an authority in your industry. Provide expert information, analysis, research that will attract users’ attention and trust. Create a profile of the author of a given post with a custom subpage aggregating all publications, with a bio and photo. It will also be good to make sure the author is highlighted in the schema.org code.
 Piotr Jacek
Piotr Jacek  Natalia Golisz
Natalia Golisz