Duplicate content is a significant problem that can lead to lower visibility of subpages and thus significantly decrease organic traffic to a site. Check out how to find duplicate content and deal with it efficiently.
What is duplicate content?
.
Duplicate content is a phenomenon that involves duplicate (duplicate) content on subpages within a single site – internal duplication; or on different external sites – external duplication. Thus, when the same content appears under different URLs, then we are dealing with a phenomenon also known as duplicate content.
Duplication can occur as a result of a mistake, theft of content or through the creation of errors at the stage of technical SEO optimization of a website or online store.
The problem of external duplication of content in the e-commerce sector usually boils down to the thoughtless copying of product descriptions or categories from manufacturers’ websites.
Internal duplication is usually encountered as a result of the publication of identical descriptions that relate to products that differ only in details – such as size or color.
What is the difference between content duplication and cannibalization?
.
The difference between content duplication and keyword cannibalization is quite important.
Content duplication is any unavoidable (identical) content that appears at more than one URL. In other words: content duplication occurs when the same larger piece of text appears on two, three or more pages within a site or between different sites.
Keyword cannibalization occurs when different subpages with different content are published within one site, which are optimized for the same keyword phrases.
Keyword cannibalization is a phenomenon that can only affect one site. Duplication of content can arise both within a single site and between external sites.
What’s more, content duplication can simultaneously result in keyword cannibalization (the same key phrases in the same content). However, phrase cannibalization does not simultaneously lead to content duplication (same key phrases, different content).
Does content duplication hurt SEO?
.
Definitely yes, duplication of content harms SEO. And it does a lot. Duplicate content negatively affects the visibility of pages with duplicate content and can result in lowering the site’s position in organic search results.
Why does duplicate content hurt SEO? Google’s algorithms, crawling several URLs of a site with the same content, do not know which subpage is more important and which they should show higher in search results.
As a result, Google can behave in several ways.
- First, Google’s algorithms may show all the URLs side by side, but in decidedly lower positions (e.g., on the 2nd, 3rd or even 4th page).
- Secondly, Google may select only one URL at its whim and display it higher relative to the other URLs with duplicate content. This solution may lead to users displaying a URL that is not necessarily the right one at the top of the search results.
- Third, Google may simply ignore any URL with duplicate content, leading to a drop in the rating of the entire site.
.
.
Regardless of how Google treats sub-pages with duplicate content, you can be sure that its reaction will negatively affect your site’s visibility, reduce organic traffic and may disrupt the customer’s path through the funnel, thereby reducing conversion rates.
The causes of content duplication
.
The problem of content duplication is quite complex and can affect online stores, blogs, portals, as well as business card sites. In fact, duplicate content can be encountered by anyone who publishes content online.
So what are the causes of content duplication? Among the most common are:
- improperly executed pagination (among other things, failure to implement self-canonicals on each pagination subpage),
- duplicated category and product descriptions,
- incorrect implementation of SSL certificate,
- appearance of subpages under different URLs,
- incorrect implementation of language versions on the site,
- developer page indexing,
- Incorrect GET parameters,
- copy large chunks of content from other subpages (inside and outside the site),
- duplication of meta tags,
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Incorrectly executed pagination
.
A poorly done pagination can lead to many problems both in terms of UX and SEO. Pagination is usually used to divide sub-pages of categories with a large number of products or to divide extensive publications.
More often than not, the pagination problem is due to poorly executed sub-page redirection.
For example, the first page with pagination may be available at two addresses:
- senuto.com/en/category
- senuto.com/en/category?p=1
.
.
Then there is a duplication of the content of the entire subpage.
The problem of incorrect pagination can be solved by creating a 301 redirect from the duplicate address, that is, the address senuto.com/en/en/category?p=1 should be redirected to senuto.com/en/category. However, it is worth changing the script so that the p=1 parameter does not appear in the URL.
Duplicate category and product descriptions
.
Duplication of product and category descriptions is one of the most common problems. Duplication of content on category subpages can occur through duplicate content as a result of pagination or when setting filters or sorting products within a category.
In this case, you can also implement a link tag with the rel attribute set to a canonical value. We use it on duplicate pages and include a link to the main category page in the code.
Duplication of product descriptions usually occurs when a product offering includes many items that do not differ significantly – for example, wires of different lengths or flat bars of varying dimensions.
A rel=”canonical” tag, which will be placed on each duplicate product page and point to the main product, can also be a solution to such a situation. An alternative solution may be to implement a feedback or comment section. These will allow users to enrich the content on product pages with unique content, which will reduce or completely eliminate the problem of duplicate content.
Duplicate content of category and product descriptions can also occur as a result of copying it from the manufacturer’s website. In such a case, make sure that the content on your site is 100% unique.
Incorrect SSL certificate implementation
.
When implementing an SSL certificate to your site, be sure to perform a redirect from HTTP to HTTPS in all URLs. A common mistake is to either not perform such a redirect, or to perform it only on a few selected addresses (e.g., only on the home page).
In this case, to avoid duplicate content, implement a global redirect of all URLs from HTTP to HTTPS.
Publication of subpages under different URLs
.
The publication of subpages of a site under different URLs can arise due to major or minor technical errors.
Most often, the creation of duplicate subpages is due to:
- appearance of the same products in different product categories (the URL contains the names of categories, so the product has different addresses),
- linking to the same page with and without “.html”,
- appearance of categories in different places in the structure of the online store,
.
.
.
In each of the described cases, the solution is to perform a 301 redirect from duplicate subpages to the correct URL.
Incorrect implementation of language versions on the site
.
Duplication of content as a result of implementing language versions on a site arises when not all subpages are translated. Then in the foreign-language version of the site there may appear text published in Polish, for example – the same text that is already on the “original” site.
To solve this problem, publish unique translated content on each of the subpages to be displayed in a foreign language. On the other hand, when a particular sub-page is not to be displayed in a particular language, then you can use the “noindex” tag.
Indexing a development site
.
Sometimes, by accident, a developer page is indexed before it is actually published.
If the website is not yet ready, then the development version should be blocked from indexation by introducing the “noindex” tag.
Invalid GET parameters
.
GET parameters are used to transfer data between successive sub-page views in the HTTP protocol. The strings “type=new” or “sort=up” are used to generate HTML code according to the client’s preferences.
The problem with an excessive number of GET parameters in URLs mainly affects webshops. Then, when multiple product filters are established, such URLs are created:
- senuto.com/en?type=new&sort=up&page=2,
- senuto.com/en?page=2&type=new&sort=up,
- senuto.com/en?sort=up&page=2&type=new,
.
.
.
In this situation, each of the above URLs leads to the same page. The easiest way to solve this problem is to perform canonical on the correct URL.
Copying larger chunks of content from other pages
.
Copying 1:1 large chunks of content and publishing them on your own site is not the best idea. Usually Google learns very quickly that the content has been copied and limits the visibility of the subpage that “borrowed” the content.
If the copied content comes from a sub-page of the same site, then a reduction in visibility can befall any of the sub-pages that have the unavoidable content published.
Note: duplication of content within the same site can also result from the appearance of the same text in the footer of the page. In this case, a longer piece of text from the footer can be used only on the home page and removed from the other subpages.
You can also fall victim to content duplication through no fault of your own. It is enough if someone copies content from your site and publishes it on their own. In such a situation, it is worth first trying to contact the owner of the site with a request to remove the duplicate content. It is also worth reporting the matter to the hosting provider.
.
Copying Meta Title and Meta Description tags also bears the hallmarks of duplicate content. In such a situation, unavoidable tags can contribute to lowering the visibility of the site.
The solution to this problem is simple – just create unique content for meta tags.
How to find duplicate content on your site?
.
There are several ways to efficiently find duplicate content within your own site. Some of the most common solutions include:
- manual site analysis,
- web crawlers,
- Google Search Console,
- inserting content snippets directly into the search engine,
.
.
.
.
Manual site analysis
.
This is the most time-consuming solution, which can prove to be an apt way to look for duplicate content on small websites. Nevertheless, for more extensive sites, it is worth using the other methods described below.
WebCrawlers
.
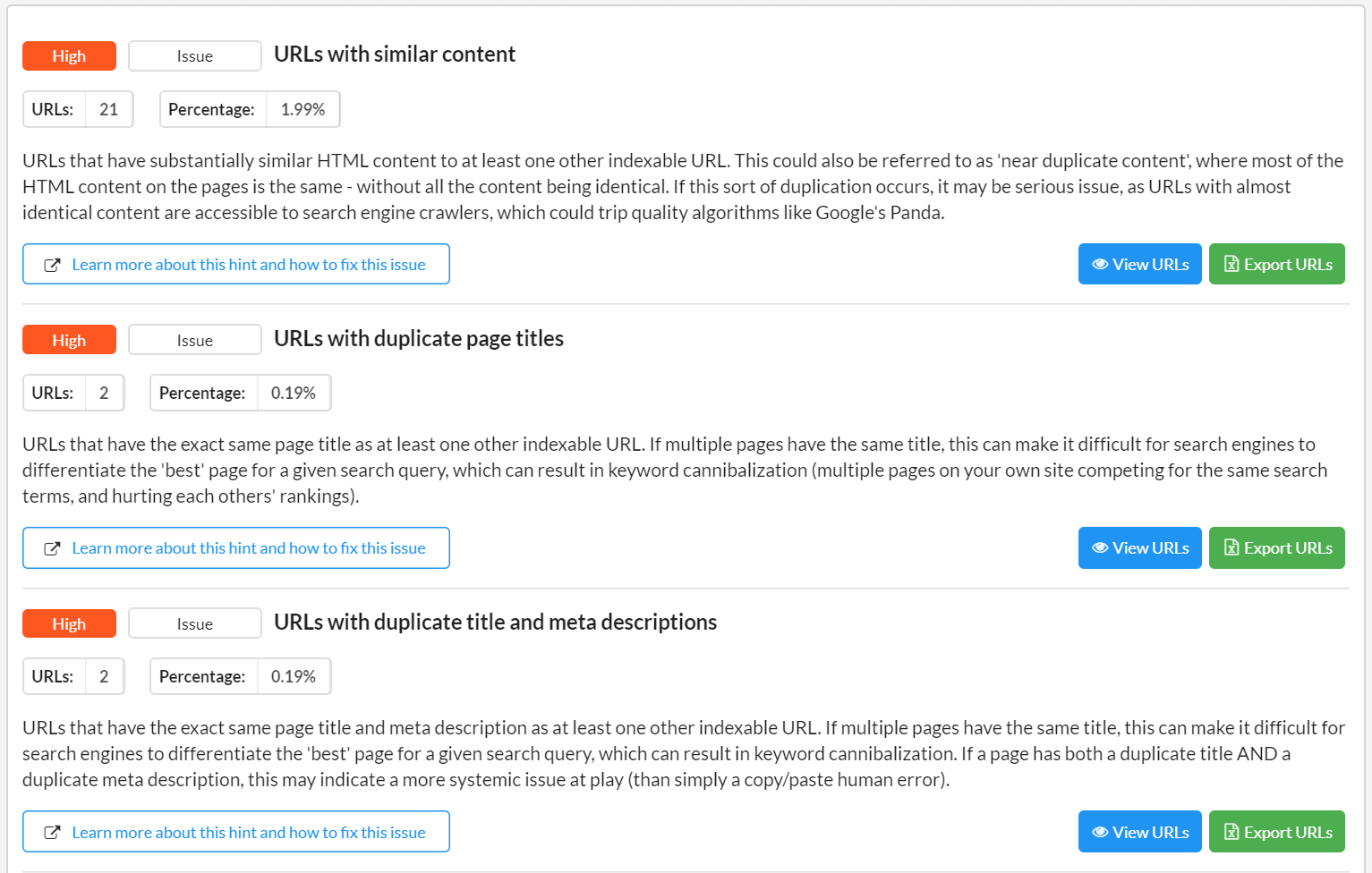
With crawlers it is possible to gather full information about the structure and content of a site. These tools are an invaluable aid when performing a website audit – including for duplicate content. Some of the most commonly used crawlers include:
- ScreamingFrog,
- Sitebulb,
- NetPeak,
- Siteliner,
- DeepCrawl,
.
.
.
.
.
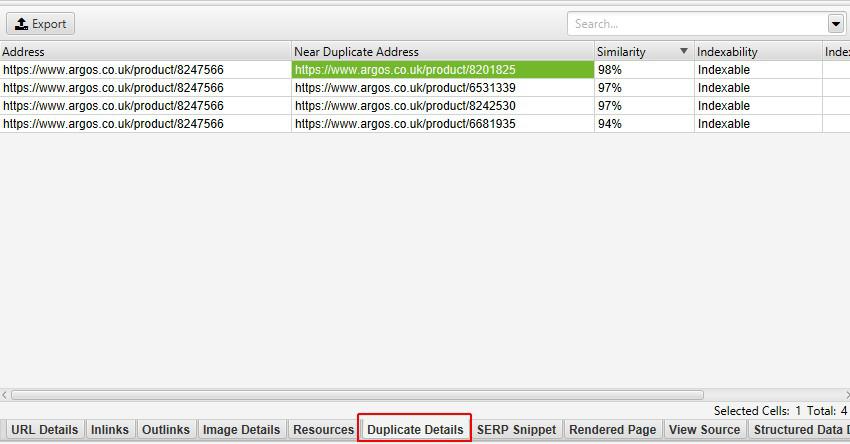
Each of the indicated crawlers makes it relatively easy to find URLs with duplicate content.
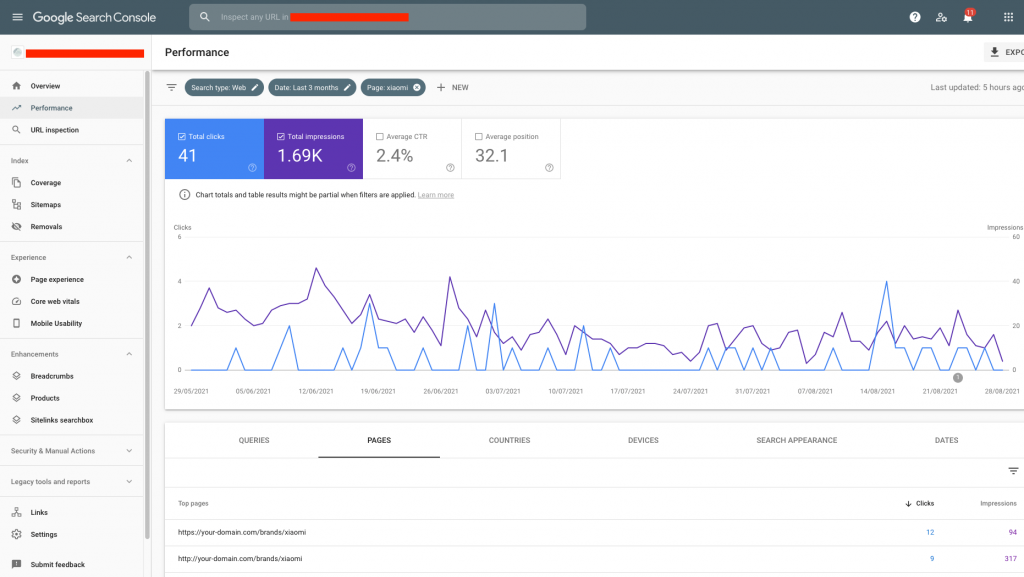
Google Search Console
.
In the Google Search Console tool, you can easily check whether a site has duplicate content. To verify duplicate content, go to the “Status” tab and then check the messages in the categories: “Error”, “Correct with warning”.
You can also go to the “effectiveness” tab and there check for duplicate URLs. For example, seemingly two different URLs, but one with http and the other with https.
Inputting content snippets into search engine
.
You can also enter snippets of duplicate content into the search engine. This solution can prove to be a good way to check key pages of your site – such as your offer tabs or blog content.
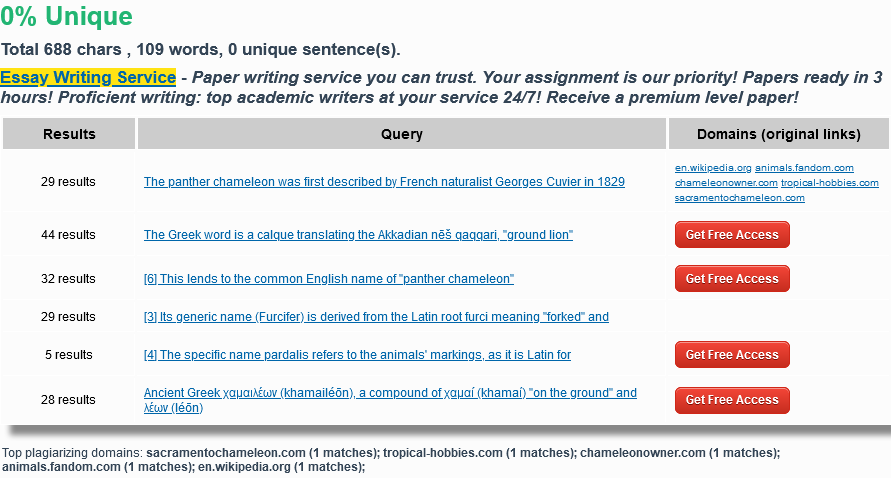
How to check for duplicate content from the web?
.
To check for duplicate content from the web, you can use one of several available tools. Among the most commonly used are Copyscape, Copywritely, Siteliner and Plagiarism. All you have to do is paste in a piece of content or a URL, and the selected tool will search for the content on the Web.
Alternatively, you can also paste a snippet of text directly into a search engine and see what results Google returns.
How to fix the problem of duplicate content?
.
The problem of duplicate content can be fixed in several ways. One of them is to perform 301 redirects from duplicate subpages to the correct URLs. With this solution, it is possible to preserve the power of duplicate subpages, since the duplicate is not removed. At the same time, 301 redirects are easy to perform.
Another solution is to implement the rel=”noindex” tag, thereby blocking the sub-page from being indexed by Google. Remember, however, that by using the “noindex” tag, you will lower the visibility potential of your site.
The third way is to use the rel=”canonical” metatag. Canonicals work great, for example, when publishing a large number of product pages with identical or nearly identical descriptions. By using canonical URLs, you will indicate to Google which URL is the most representative among a set of duplicate subpages.
In the case of duplicate content resulting from the implementation of different language versions of the site, it is definitely worth using the “hreflang” tag. By doing so, you will indicate to Google the differences between different language versions of the site.
The problem of duplicate content can also be solved by creating and publishing unique content on each duplicate subpage.
Summary
.
Duplicate content is a significant problem that especially affects larger stores and websites. It is worthwhile to regularly verify that there is no duplication of external and internal content, and quickly take appropriate action to eliminate the problem. Duplicate content can significantly reduce a site’s visibility in search results, and thus lead to a drop in organic traffic.
 Marcin Cichocki
Marcin Cichocki